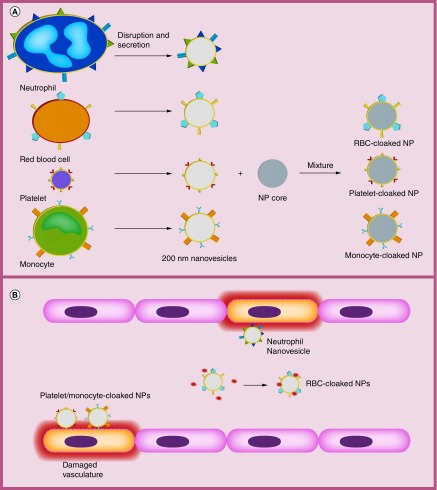
Figure 1. . Schematic of general preparation of membrane-coated nanoparticles and inflamed vasculature.
(A) Specific preparation of NPs varies depending on study but overall process remains the same to generate empty membrane nanovesicles. Vesicles are extracted from parent cells such as neutrophils, RBCs and platelets by disruption/secretion. These membrane-derived vesicles that retain the cell membrane antigens of parent cells can be combined with a nanoparticle core to form the final camouflaged nanoparticle. (B) Neutrophil, platelet and monocyte membrane-camouflaged nanovesicles can directly target and bind inflamed vasculature. RBC membrane-camouflaged nanovesicles can absorb cell membrane-damaging toxins (PFTs) in blood.
NP: Nanoparticle; PFT: Pore-forming toxin; RBC: Red blood cell.