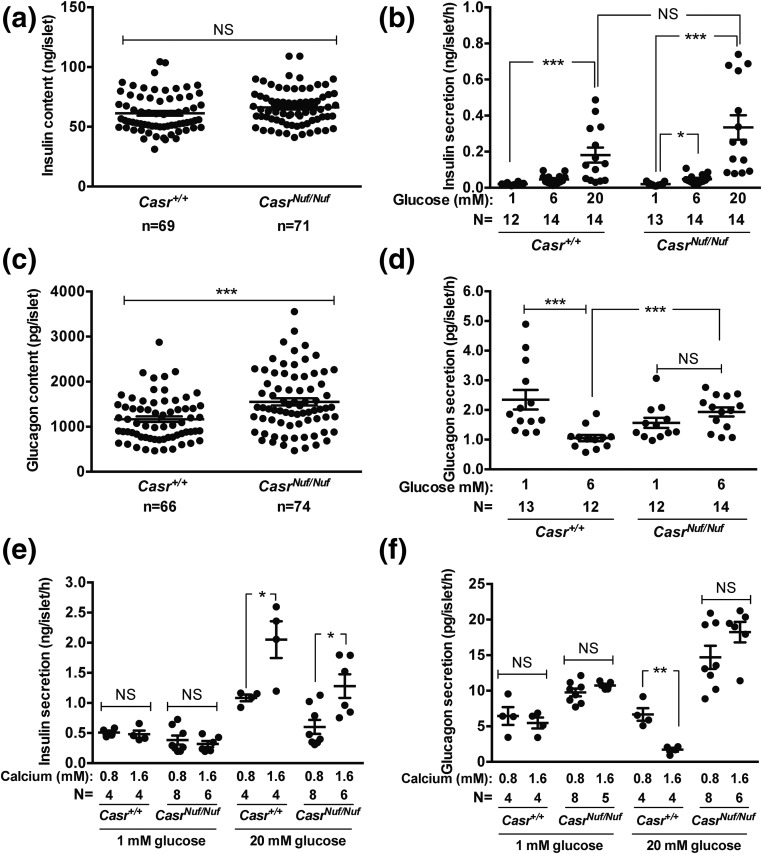
Figure 6.
Insulin and glucagon secretion from isolated Nuf mice pancreatic islets. (a) The total insulin content of CasrNuf/Nuf islets was not altered compared with Casr+/+ islets. (b) Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets were incubated in 1.6 mM [Ca2+]o and exposed to varying glucose concentrations (1, 6, or 20 mM). Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets showed significantly increased insulin secretion following stimulation with 20 mM glucose. No significant differences in the maximal insulin secretory responses were observed between Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets. (c) The total glucagon content of CasrNuf/Nuf islets was significantly increased compared with Casr+/+ islets. (d) Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets were incubated in 1.6 mM [Ca2+]o and exposed to 1 and 6 mM glucose concentrations. Casr+/+ islets showed a significant reduction in glucagon secretion following stimulation with 6 mM glucose. In contrast, glucagon secretion from CasrNuf/Nuf islets failed to suppress following glucose stimulation, and CasrNuf/Nuf islets had significantly increased glucagon secretion compared with Casr+/+ islets at 6 mM glucose. (e) The effect of Ca2+o on insulin secretion was assessed by incubating Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets with varying Ca2+o concentrations (0.8 or 1.6 mM) and exposing them to low (1 mM) or high (20 mM) glucose. Exposure to low (0.8 mM) Ca2+o suppressed insulin secretion from Casr+/+ and CasrNuf/Nuf islets at 20 mM glucose. (f) Exposure to low (0.8 mM) Ca2+o increased glucagon secretion from Casr+/+ islets at 20 mM glucose but had no effect on glucagon secretion from CasrNuf/Nuf islets. Islet insulin and glucagon in panels (a–d) were measured by radioimmunoassay and by duplex rat/mouse ELISA (Meso Scale Discovery) in panels (e) and (f). The sample size (N) represents batches of size-matched islets, which were pooled from three to six Casr+/+ mice and six CasrNuf/Nuf mice. Mean ± standard error of the mean values for the respective groups are indicated by solid bars. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. NS, nonsignificant.