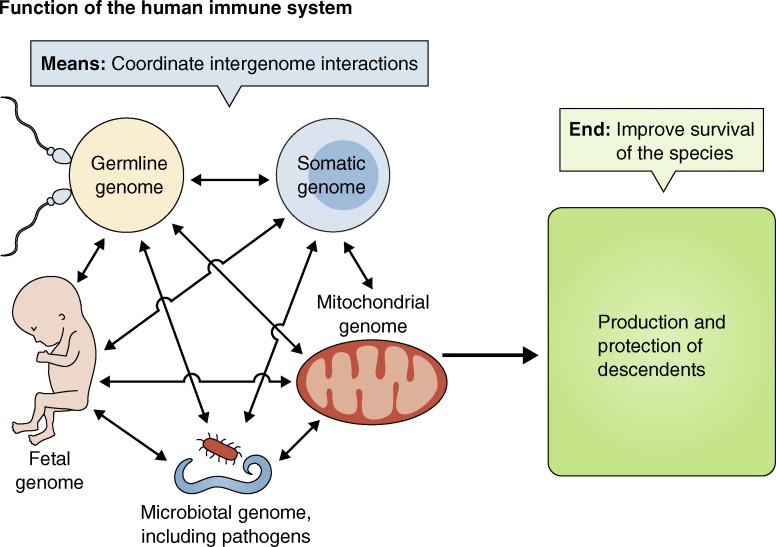
Figure 1.
Function of the human immune system. The immune system is the set of cellular and soluble factors by which the germline genome interacts with the somatic, mitochondrial, fetal, and microbiotal genomes to protect the individual’s ability to propagate the species. Arrows between genomes signify epigenetic, transcriptional, and posttranscriptional influences on expression of genes in one genome of an individual by the alleles present in the individual’s other genomes.