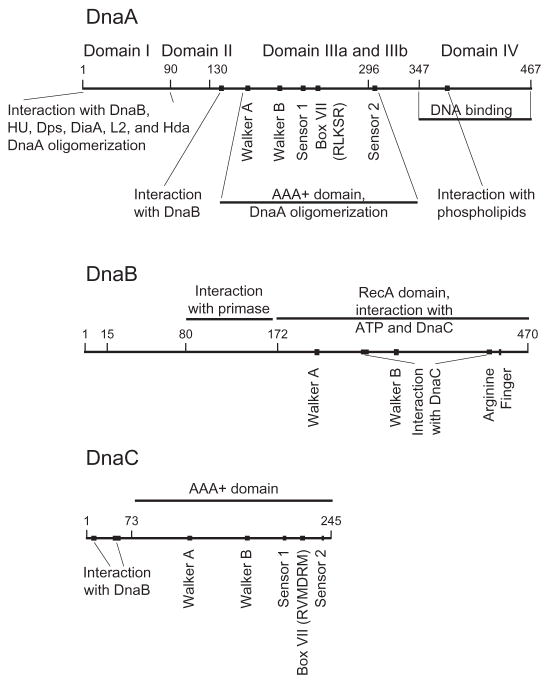
Fig. 2.
Domain organization of DnaA, DnaB, and DnaC protein. The numbers in the respective lines refer to the coordinates for E. coli DnaA, DnaB, and DnaC protein. DnaA: Domain I interacts with DnaB, HU, Dps, DiaA, Hda, and ribosomal protein L2, and is also required for DnaA oligomerization. Domain II may function as a flexible linker to join domain I and III. Domain III carries the amino acid sequence motifs shared among AAA+ family members that act in ATP binding and its hydrolysis. This domain also functions in DnaA oligomerization, and appears to carry a site denoted by a filled square that interacts with DnaB. Domain IIIa carries an abbreviated RecA-type fold. Domain IIIb contains a three-helix bundle. Domain IV binds to the DnaA box and presumably also to I-, τ-, and C-sites. A region that interacts with acidic phospholipids is in domain IV. The borders separating the domains have been determined by functional analysis of DnaA together with a homology model based on the X-ray crystal structure of domain III and IV of A. aeolicus DnaA. DnaB: Its N-terminal domain interacts with primase and its larger C-terminal domain functions in ATP binding and hydrolysis. On the basis of the X-ray crystallographic structures of Geobacillus kaustophilus and Geobacillus stearothermophilus DnaB [82,83], this C-terminal domain that also interacts with DnaC is similar in structure to RecA. The filled symbols represent the Walker A and B boxes and the arginine finger (arginine 442 of E. coli DnaB), and the DnaC-interacting domains. DnaC: The interacting domains of DnaC with DnaB and with ATP, including the AAA+ motifs and the conserved arginines in box VII are shown. Reviewed in Ref. [42].