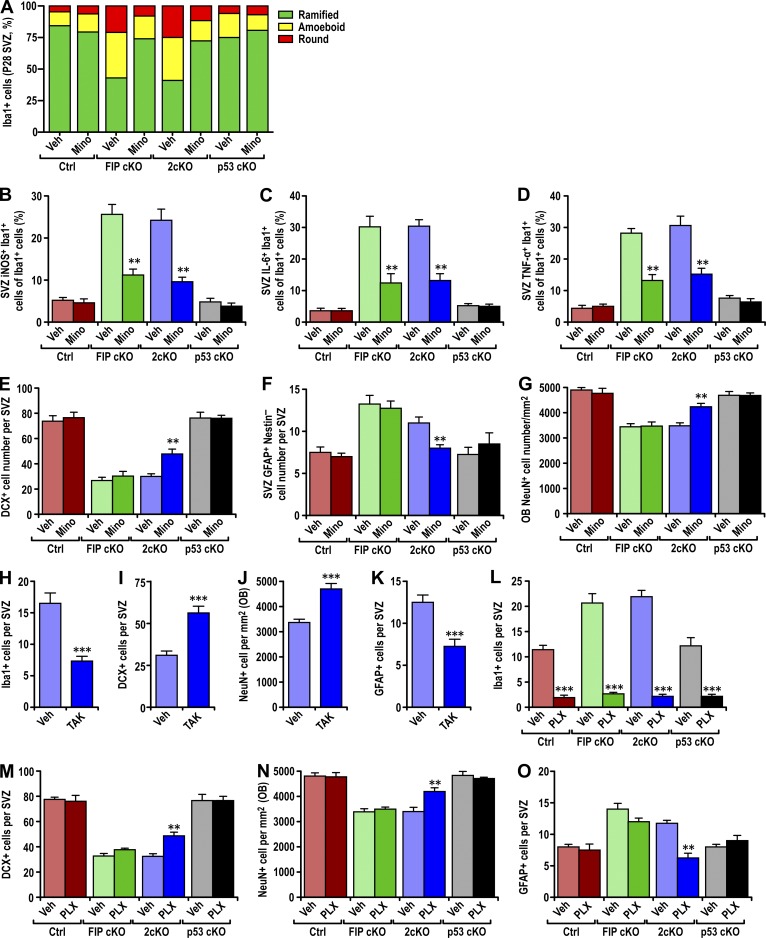
Figure 5.
Suppression of microglia activation and infiltration rescued the defective neurogenesis in 2cKO mice. (A) The percentage of ramified, round, and amoeboid microglia per SVZ section of Ctrl, FIP cKO, 2cKO, and p53 cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or minocycline (Mino; three mice each). (B–D) Number of iNOS+ microglia (B), IL-6+ microglia (C), or TNF+ microglia (D) per SVZ section in Ctrl, FIP cKO, 2cKO, and p53 cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or minocycline (Mino; mean ± SEM; three mice each). (E–G) Number of DCX+ neuroblasts (E) and GFAP+ astrocytes (F) per SVZ section or the density of NeuN+ neurons per olfactory bulb section (G) in Ctrl, FIP cKO, 2cKO, and p53 cKO mice treated with vehicle or minocycline are shown (mean ± SEM; three mice each). (H) Number of Iba1+ microglia per SVZ section of 2cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or TAK-779 (TAK; mean ± SEM; three mice each). (I–K) Number of DCX+ neuroblasts (I) and GFAP+ astrocytes (K) per SVZ section or the density of NeuN+ neurons per olfactory bulb section (J) in 2cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or TAK-779 (TAK; mean ± SEM; three mice each). (L) Number of Iba1+ microglia per SVZ section in Ctrl, FIP cKO, 2cKO, and p53 cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or PLX3397 (PLX; mean ± SEM; four mice each). (M–O) Number of DCX+ neuroblasts (M) and GFAP+ astrocytes (O) per SVZ section or the density of NeuN+ neurons per olfactory bulb section (N) in Ctrl, FIP cKO, 2cKO, and p53 cKO mice treated with vehicle (Veh) or PLX3397 (PLX) are shown (mean ± SEM; four mice each). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.