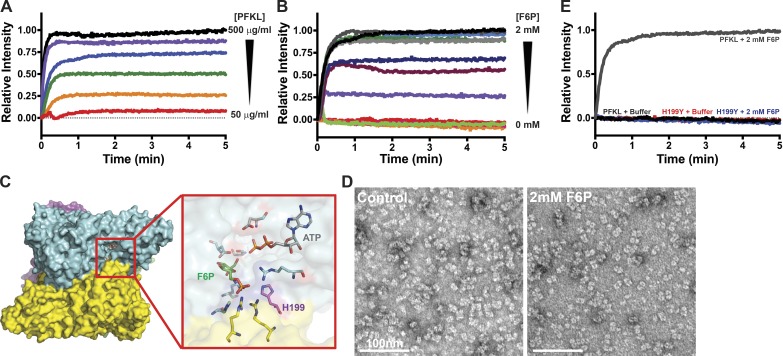
Figure 2.
PFKL filament formation is concentration- and F6P-dependent. (A) 90° light scattering of 50–500 µg/ml PFKL upon the addition of 2 mM F6P at time 0. Red, 50 µg/ml; orange, 100 µg/ml; green, 150 µg/ml; blue, 200 µg/ml; purple, 400 µg/ml; black, 500 µg/ml. (B) 90° light scattering at the 200 µg/ml PFKL upon the addition of the indicated concentration of F6P at time 0. Red, 0 mM; orange, 0.25 mM; pink, 0.5 mM; green, 0.6 mM; purple, 0.7 mM; maroon, 0.75 mM; dark blue, 0.8 mM; light blue, 0.9 mM; dark green, 1.0 mM; light gray, 1.25 mM; dark gray, 1.5 mM; black, 2.0 mM. (C) Location of His199 in the F6P binding pocket of PFK1. (D) TEM images of PFKL-H199Y in control buffer (left) and in buffer containing 2 mM F6P (right). (E) 90° light scattering at 200 µg/ml PFKL or PFKL-H199Y upon the addition of 2 mM F6P at time 0. Data are representative of three determinations from two separate protein preparations.