Figure 2.
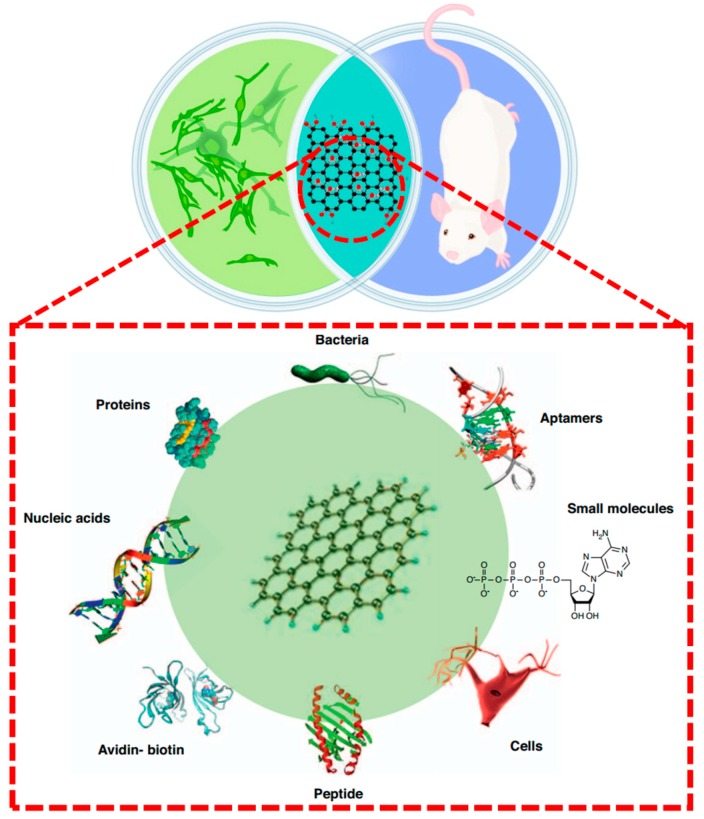
Although graphene oxide has been demonstrated to be cytocompatible in vitro, its compatibility in vivo in tissue sites relevant for biomedical device application is yet to be fully understood. Promising results may be achieved by proper functionalization. Graphene and its derivatives have been reported to be functionalized with avidin–biotin, peptides, nucleic acid, proteins, aptamers, small molecules, bacteria, and cells through physical adsorption or chemical conjugation. Reproduced from [37,45].