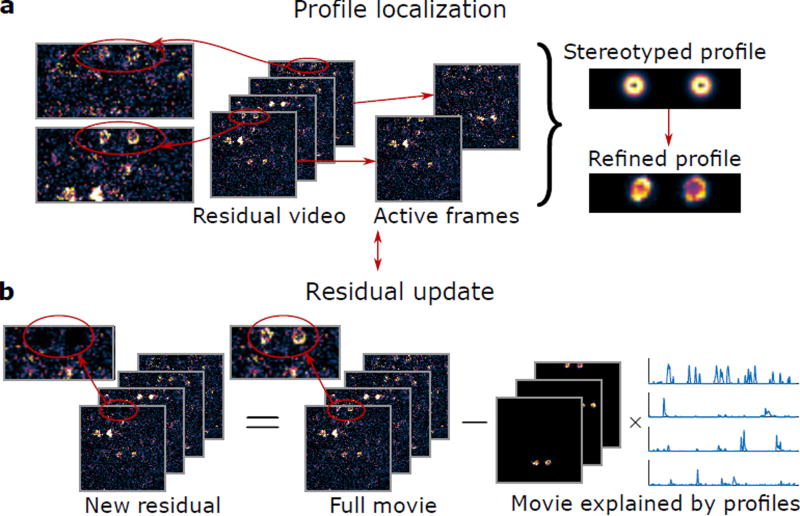
Figure 3.
Sparse convolutional iterative shape matching (SCISM) for demixing vTwINS data. (a) Example stereotyped neuron image pairs with different distances are matched across frames to determine the most likely pair. The new profile is refined by locally masking and averaging frames closely aligned with the stereotyped spatial profile. (b) The new profile is added to the set of spatial profiles, and the time-traces for all spatial profiles are calculated via non-negative LASSO. The residual movie is re-computed by subtracting the contribution of the current set of spatial profiles (the sum of outer products of the spatial profiles and their time traces). The algorithm then finds the next spatial profile by restarting and operating on the new residual.