Figure 1. CAMKIIγ is essential for T cell lymphomagenesis in vivo.
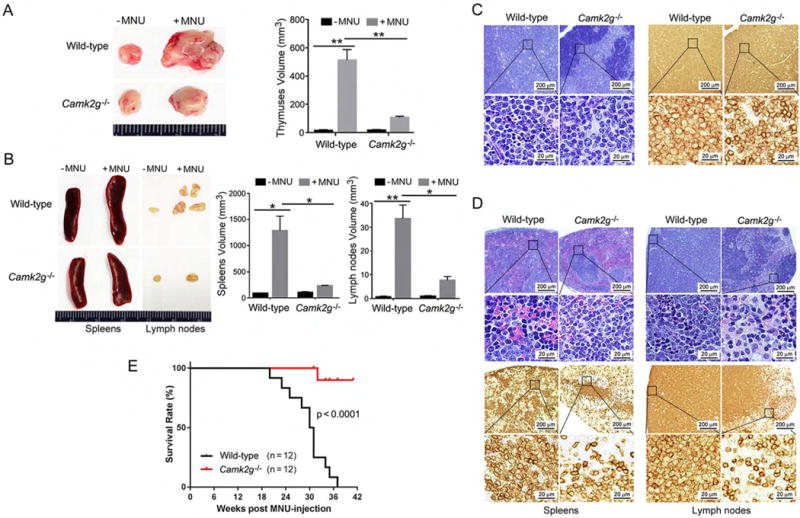
(A) Thymuses obtained from wild-type or Camk2g−/− mice 20 weeks after MNU injection or without MNU injection.
(B) Spleens and lymph nodes obtained from wild-type or Camk2g−/− mice 20 weeks after MNU injection or without MNU injection.
(C) Paraffin sections of mice thymuses in MNU-injected mice analyzed by H&E staining (left) or immunohistochemistry with murine CD3 (right).
(D) Paraffin sections of mice spleens and lymph nodes in MNU-injected mice analyzed by H&E staining (upper) or immunohistochemistry with murine CD3 (lower).
(E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for wild-type or Camk2g−/− mice after MNU injection.
Data represent the mean ± s.d. for 8 mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. See also Figure S1.
