Figure 7. Pharmacological inhibition of CAMKIIγ destabilizes the c-Myc protein and effectively reduces tumor burden.
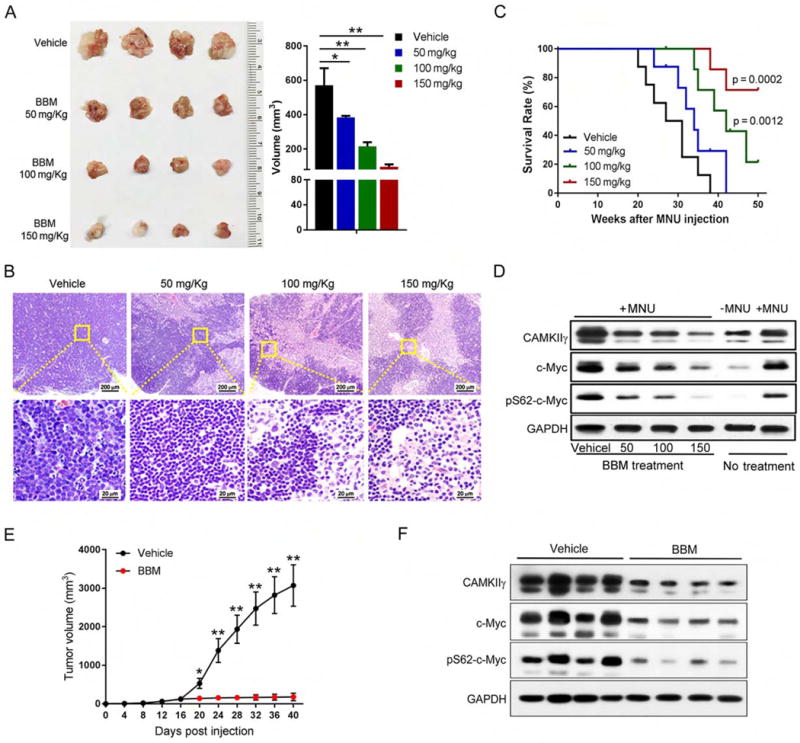
(A) Thymuses obtained from mice suffering MNU-induced lymphoma treated as indicated (n = 4).
(B) Paraffin sections of thymuses in (A) analyzed by H&E staining.
(C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of mice suffering MNU-induced lymphoma treated as indicated (n = 8 mice per group).
(D) Indicated proteins in tissue lysates from thymuses in (A) were detected using the Western blot analysis. Tissue lysates from wild-type thymuses with or without MNU injection only were shown as expression controls.
(E) Tumor volume comparison between indicated treatment groups at indicated time points after cell inoculation (n = 6 mice per group).
(F) Indicated proteins in xenografted tumor lysates from indicated treatment groups were detected using the Western blot analysis.
Data represent the mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. See also Figures S7 and S8.
