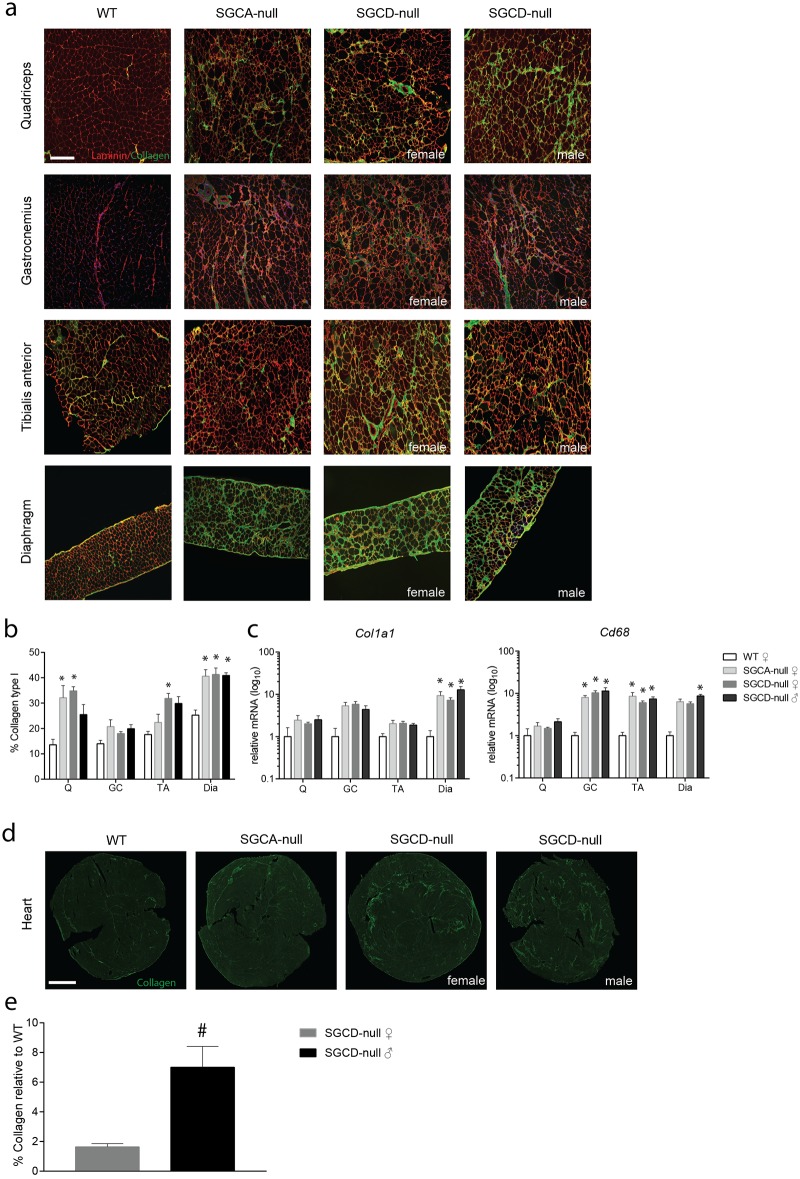
Fig 3. Elevated collagen levels in skeletal muscles in SGCA- and SGCD-null mice and in the heart of SGCD-null mice.
(a) Immunofluorescent images of skeletal muscles stained with collagen type I (fibrotic marker, green) and laminin (extracellular matrix of muscle fibres, red) Scale bar: 100 μm. (b) Quantification of collagen type I positive area in skeletal muscles relative to wild type muscles. A significant increase in the percentage of collagen type I positive area was found in diaphragm and quadriceps muscles of SGCA- and SGCD-null mice, while no difference was found in the gastrocnemius. Tibialis anterior muscles of female SGCD-null mice showed a significant increase in collagen type I positive area compared to wild type. (c) Fibrotic and inflammatory gene expression measured by qPCR, normalized to Gapdh (n = 5 mice per group) in skeletal muscles of LGMD and wild type mice. A significant increase in Col1a1 and Cd68 expression was found in SGCA- and SGCD-null muscles when compared to wild type muscles. (d) Immunofluorescence images of the heart stained with collagen type I (fibrotic marker, green). Scale bar: 1000 μm. (e) The percentage of collagen type I positive area, measured with Image J was significantly increased in SGCD-null mice compared to wild type mice; males showed a significantly higher increase in collagen than did female SGCD-null mice. Q, quadriceps; GC, gastrocnemius; TA, tibialis anterior; Dia, diaphragm. * Indicates a significant difference from WT controls. # Indicates a significant difference from female SGCD-null mice. Error bars represent ± SD.