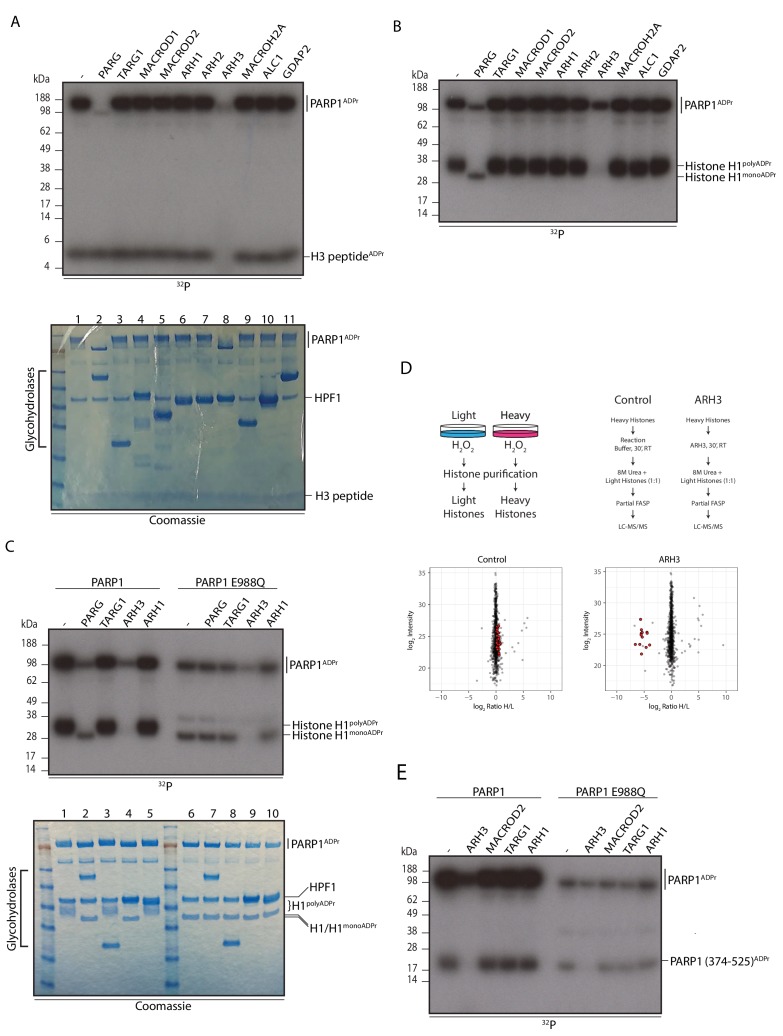
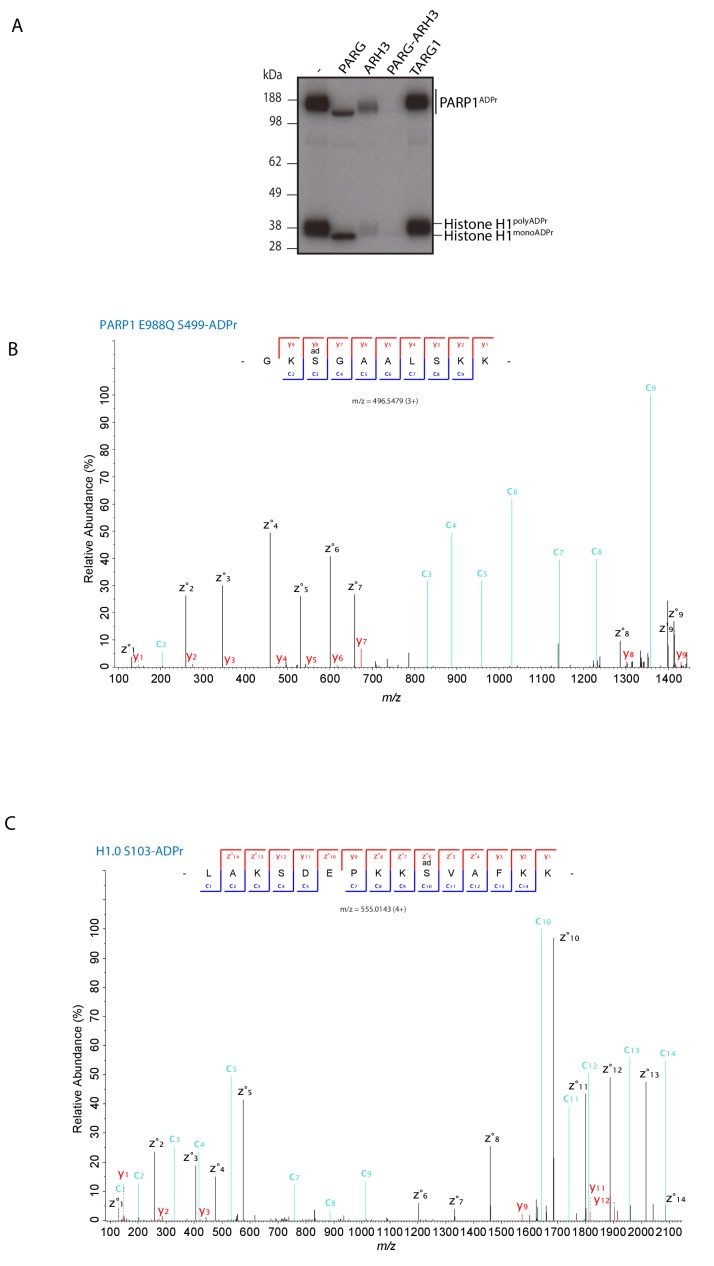
Figure 2. ARH3 hydrolyses Ser-ADPr.
(A) Glycohydrolysis of mono-ADP-ribosylated H3 histone peptide (aa 1-21). ADP-ribosylated H3 peptide was obtained by incubation with PARP1 and HPF1 using radioactively labelled NAD+ as an ADPr donor. After stopping the modification reaction with PARP inhibitor, the indicated glycohydrolases and related proteins were added to the substrate as shown on the figure. Lower panel – Coomassie stained gel of the proteins used in the reaction that also serves as a loading control. (B) Removal of poly-ADP-ribosylation from the recombinant histone H1 substrate by various glycohydrolases. Reaction performed as described in A. (C) Comparison of the hydrolase reactions on the poly- and mono-ADP-ribosylated histone H1 substrates. Lower panel – Coomassie stained gel of the proteins used in the reaction that also serves as a loading control. (D) Schematic representation of the SILAC-based strategy to quantify ADPr removal upon in vitro incubation of purified Ser-ADPr histones with or without recombinant ARH3 (top panels). Log2 of summed peptide intensities were plotted against log2 Heavy/Light SILAC ratios for each condition (bottom panels). ADPr peptides are colored in red. (E) Autoradiogram analysis of Ser mono-ADPr hydrolysis with a non-histone protein substrate. The ADP-ribosylated automodification domain of PARP1 (aa 374-525) was used in this assay and the reactions were supplemented with the indicated hydrolases. In panel panels A, B, C and E, the reaction products were separated by SDS-PAGE and analysed by autoradiography. The signals relating to the specific ADP-ribosylated protein are indicated in each panel.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28533.006