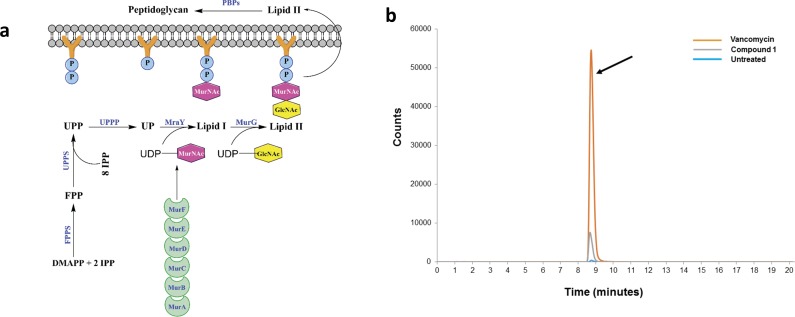
Fig 6. Simplified pathway for bacterial cell wall synthesis.
(a) Diagram of key reactions in peptidoglycan synthesis for bacterial cell wall. Abbreviations: MurA, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase; MurB, UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase; MurC, UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine synthetase; MurD, UDP-N-acetylmuramyl-l-alanine:d-glutamate ligase; MurE, UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanyl-d-glutamate:meso-2,6-diaminopimelate ligase, MurF, UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-tripeptide-D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase, MurG, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-N-acetylmuramyl-(pentapeptide) pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol N-acetylglucosamine transferase; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; FPP, isoprenoid farnesyl diphosphate; FPPS, farnesyl diphosphate synthase; UPP, C55 isoprenoid undecaprenyl diphosphate; UPPS, undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase; UPPP, undecaprenyl diphosphate phosphatase; UP, undecaprenyl monophosphate; MraY, phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; MurNAc, N-acetylmuramic acid; PBPs, penicillin-binding proteins. (b) Detection of final soluble cell wall precursor (UDP-N-acetylmuramyl pentapeptide) inside bacterial cytoplasm. HPLC chromatogram of S. aureus NRS107 (RN4220) treated with 10 × MIC of compound 1 or vancomycin for 30 minutes. After centrifugation, the bacterial pellet was boiled for 30 minutes to release contents present in the bacterial cytoplasm. The lysate was analyzed using HPLC/MS, using a phenyl column, to determine the accumulation of the final soluble precursor in cell wall synthesis, UDP-N-acetylmuramyl pentapeptide (designated by the black arrow).