Figure 6. Treatment with CTLA4-Ig and oATP inhibited chronic rejection and induced long-term heart allograft survival.
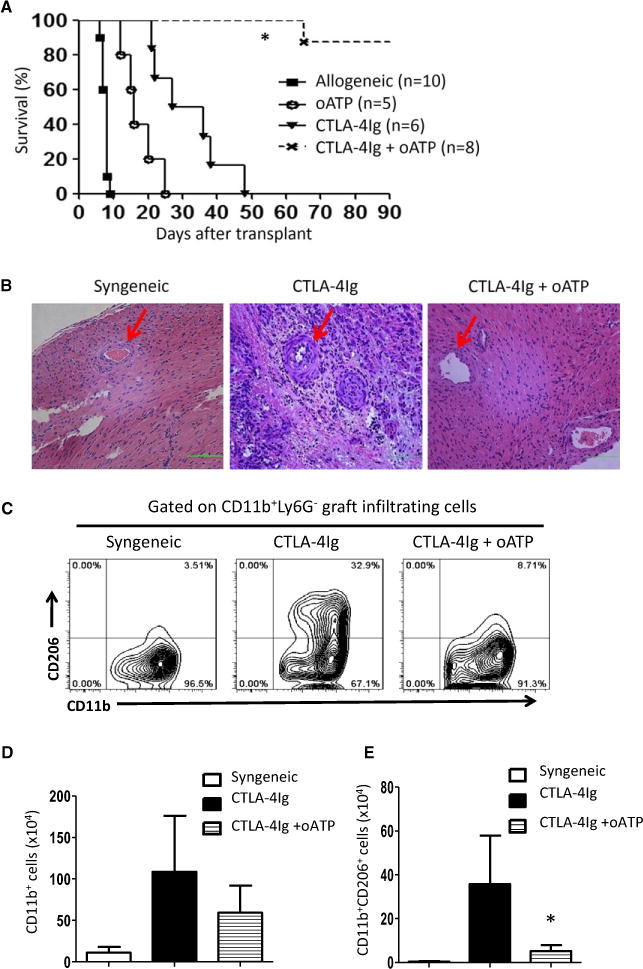
(A) Survival curves for Balb/c heart allografts in B6 recipients treated with CTLA4-Ig, oATP or a combination of CTLA4-Ig and oATP. (B) Sections of hematoxylin and eosin staining of heart transplants from recipients treated with CTLA4-Ig alone or combined CTLA4-Ig and oATP showing vascular changes and tissue damage. Arrows indicate small arteries in the graft. Syngeneic heart transplants were used as controls for comparison. (C) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting plots showing CD206+ cells among CD11b+ graft-infiltrating cells in recipient mice treated with CTLA4-Ig or combined CTLA4-Ig and oATP 30 days after transplantation. (D) The number of CD11b+ cells retrieved from heart allografts. Data shown are mean ± SE of three transplants in each group. (E) The number of CD11b+CD206+ cells from heart allografts is shown. Data shown are mean ± SE of three transplants in each group. (*p < 0.05). CTLA4-Ig, CTLA4 immunoglobulin fusion protein; oATP, oxidized adenosine triphosphate; SE, standard error.
