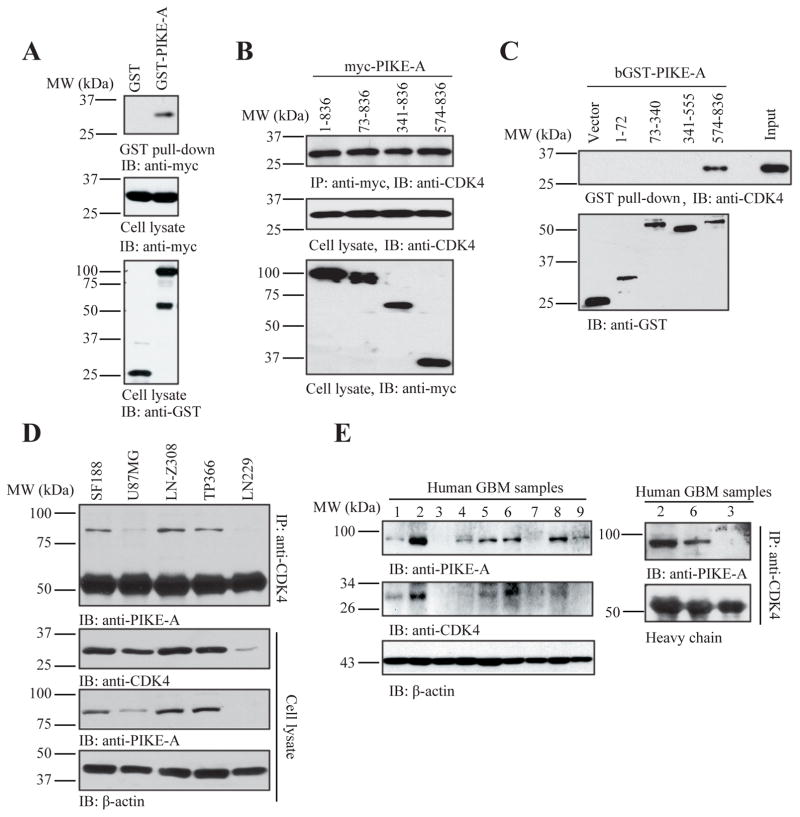
Figure 4. PIKE-A interacts with CDK4 in vitro and in vivo.
A. GST-pull down assay for PIKE-A binding to CDK4. Cell lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with GST-tagged PIKE-A and Myc-tagged CDK4 were collected and analyzed by GST-pull down assay as described in Experimental procedures. Data indicated that PIKE-A interacted with CDK4 in cells compared to GST vector control. B & C. Truncation analysis indicates that the C-terminus of PIKE-A (a.a. 574–836) binds to CDK4. Cell lysates were collected from TP366 cells transfected with myc-tagged PIKE-A truncations and used for co-immunoprecipitation analysis with anti-myc antibody (B). Purified GST-tagged PIKE-A truncated recombinant proteins confirmed that C-terminus of PIKE-A (a.a. 574–836) interacted with CDK4 in GST pull-down assay (C). D. Interaction of PIKE-A and CDK in glioblastoma cells. Glioblastoma cells were collected and lysed for co-immunoprecipitation. Endogenous CDK4-associated proteins were collected by anti-CDK4 antibody and analyzed by indicated antibodies. E. Interaction of PIKE-A and CDK in human glioma tissues. Expression profiles of PIKE-A or CDK4 in human glioblastoma tissues (left panels). Co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed using the lysates form human glioma tissues with different PIKE-A expression levels. The CDK4-associated proteins were analyzed by western blotting showing that PIKE-A interacted with CDK4 (right panels).