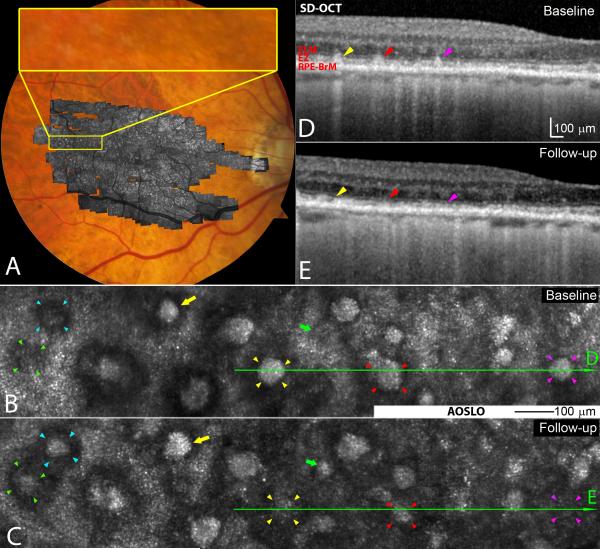
Figure 1.
Subretinal drusenoid deposit (SDD) dynamism imaged by multimodal imaging. A. Adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (AOSLO) montage (in grey scale) is overlaid on the digital fundus photograph of 30° field of view. B & C. AOSLO images of the retina area shown in the yellow box in (A) taken at baseline and 2nd visit (14 months later), revealing SDD progression. A stage 1 lesion progressed to stage 3 (green arrowheads 5), and a stage 2 lesion progressed to stage 3 (aqua). Stage 3 lesions may expand (yellow arrows), shrink (red arrowheads), and disappear (yellow and magenta arrowheads). New lesions can develop (green arrows). D & E.Stage-specific changes in SDD appearance are also clear in corresponding spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) B-scans, as indicated by green lines with arrows in (B) and (C). Stripes of hypertransmission into the choroid indicating retinal pigmetal epithiulium degeneration are apparent,15 as will be described in a separate report.60 The subject is an 84-year-old (at the baseline study) woman (white non-Hispanic) with non-neovascular AMD (Age-Related Eye Disease Study grade 7, best-corrected visual acuity 20/20). An alternate labelling scheme not using color is available as Supplemental Digital Content 2. ELM: external limiting membrane. EZ: ellipsoid zone. RPE-BrM: retinal pigment epithelium-Bruch’s membrane.