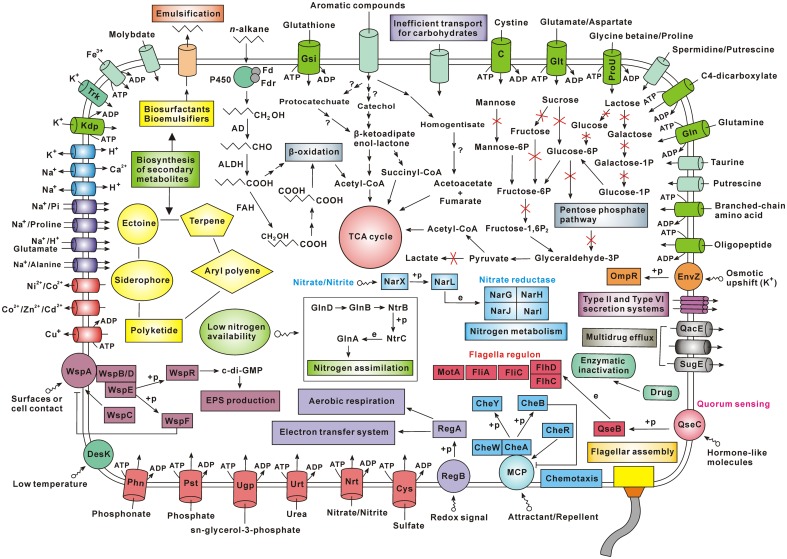
FIGURE 6.
Schematic overview of the metabolism and material transport in Achromobacter sp. HZ01. Primary information: (i) the n-alkane degradation in strain HZ01 is performed via the terminal oxidation pathway, and the catechol pathway may play a major role in the degradation of aromatic compounds; (ii) the inefficient carbohydrate transport and the lack of some key enzymes account for the bacterial inability to utilize several common carbohydrates for growth; (iii) strain HZ01 harbors the genes related to biosynthesis of secondary metabolites; (iv) the membrane transporters are essential for nutrient uptake and substance export; (v) strain HZ01 contains important two-component systems for the responses to environmental changes; (vi) the chemotaxis and flagellar assembly are beneficial for pursuing nutrients and avoiding environmental damages; (vii) besides through the enzymatic inactivation of antibiotics, strain HZ01 contains efflux pumps for elimination of antibiotics. Not all the metabolic pathways and transporters are shown in the figure. Import or export of solutes is indicated by the direction of the arrow through the transporter. The arrow with a red X shape indicates that the metabolic step is absent. The arrow with a question mark indicates that it is unsure whether the corresponding step can be completed. Abbreviations: Fd, ferredoxin; Fdr, ferredoxin reductase; P450, cytochrome P450; AD, alcohol dehydrogenase; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; FAH, fatty acid hydroxylase; +p, phosphorylation; e, expression; Trk, potassium transporter Trk; Kdp, Kdp system for potassium transport; EPS, extracellular polysaccharide; Phn, phosphonate transport system; Pst, phosphate transport system; Ugp, sn-glycerol-3-phosphate transport system; Urt, urea transport system; Nrt, nitrate/nitrite transport system; Cys, sulfate transport system; MCP, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein; Gln, glutamine transport system; ProU, glycine betaine/proline transport system; Glt, glutamate/aspartate transport system; C, cystine transport system; Gsi, glutathione transport system.