Figure 7.
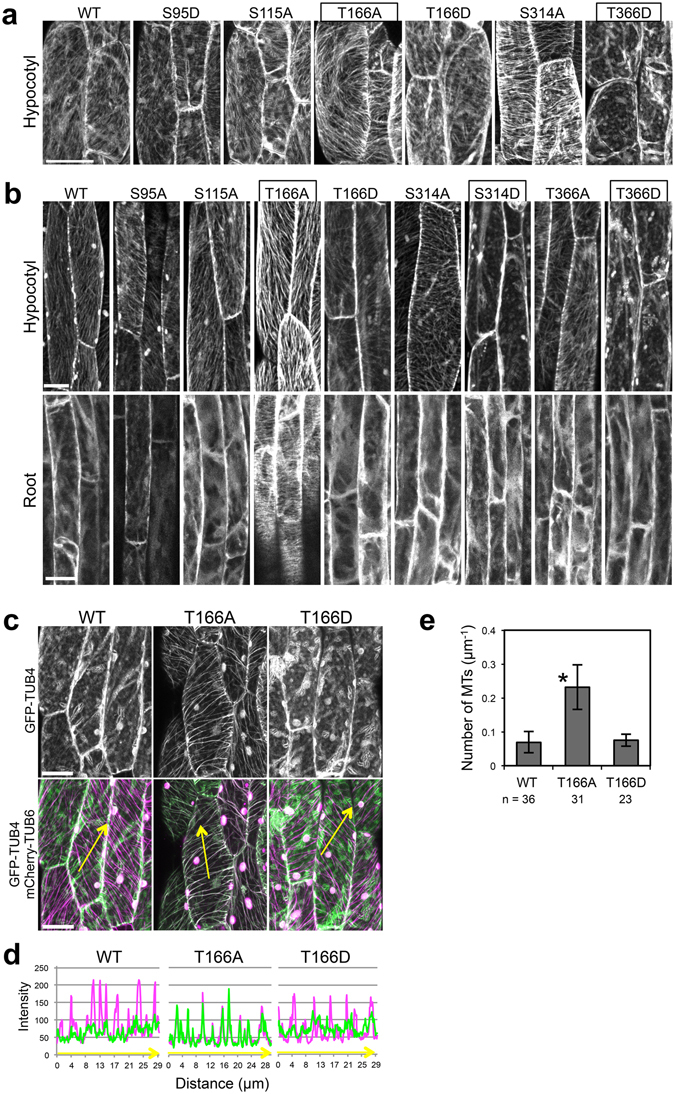
Involvement of Thr166 of β-tubulin in cortical microtubule depolymerization. (a,b) Subcellular localization of wild type TUB4 (WT) and mutated TUB4 proteins (S95A, S115A, T166A, T166D, S314A, S314D, T366A and T366D) fused with GFP at the N-terminus. GFP-TUB4 was constitutively driven by the CaMV35S promoter in (a) (35S:GFP-TUB4) or expressed under the TUB4 own promoter in (b) (TUB4pro:GFP-TUB4). The scale bars represent 30 µm in (a) or 20 µm in (b). (c) Subcellular localization of wild type TUB4 (WT) and mutated TUB4 proteins (T166A or T166D) fused with GFP at the N-terminus (green). Cortical microtubules are visualized with mCherry-TUB6 (magenta). The scale bars represent 20 µm. (d) Profiles of fluorescence intensity of GFP and mCherry along lines shown in (c). (e) Density of microtubules labeled with the wild type TUB4 (WT) or mutated TUB4 (T166A or T166D) fused with GFP. Data are displayed as averages ± SD. The asterisk indicates significant difference from the value in wild type GFP-TUB4 (t-test, P < 0.001).
