Fig. 5.
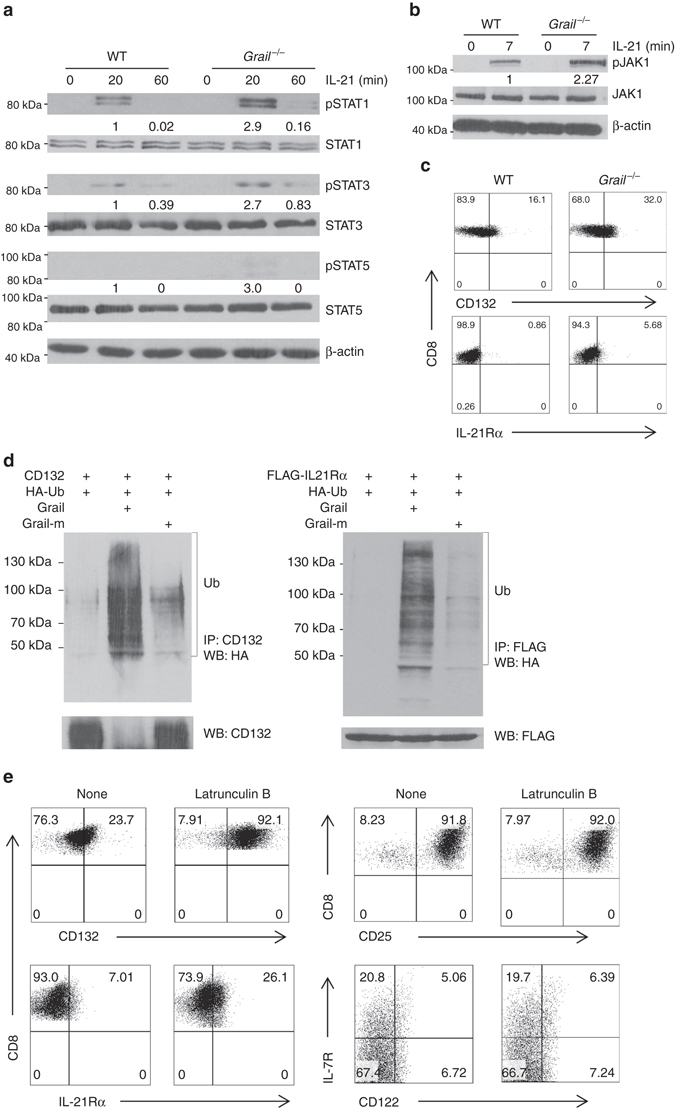
Grail ubiquitinates the IL-21 receptor. a FACS-sorted naive WT and Grail −/− CD8+ T cells were treated with or without IL-21 for the indicated time points (0–60 min). The whole cell lysate was subjected to western blot assay to detect the levels of phosphorylated and total STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5. β-actin was used as a loading control. b Naive WT and Grail −/− CD8+ T cells were treated with or without IL-21 for 7 min, followed by western blot to detect the phosphorylated and total JAK1 levels. β-actin was used as a loading control. c γC (CD132) and IL-21Rα protein levels on the surface of naive untreated WT and Grail −/− CD8+ T cells. Numbers in dot plot quadrants represent the percentages of each subset. d About 293T cells were transfected with vectors encoding CD132 or IL-21Rα, HA-Ub, and either Grail or a Grail mutant (Grail-m). The lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (i.p.) using an anti-FLAG or anti-CD132 antibodies. The blots were probed with anti-HA-HRP and re-probed with anti-FLAG or anti-CD132. e Naive WT and Grail −/− CD8+ T cells were activated with OVA peptide and irradiated WT APCs alone or with Latrunculin B. γC (CD132), IL-21Rα, CD25, CD122 and IL-7R expression on CD8+ T cells were assessed 48 h after activation. Numbers in dot plot quadrants represent the percentages of each subset. All experiments were independently performed three times
