Figure 2.
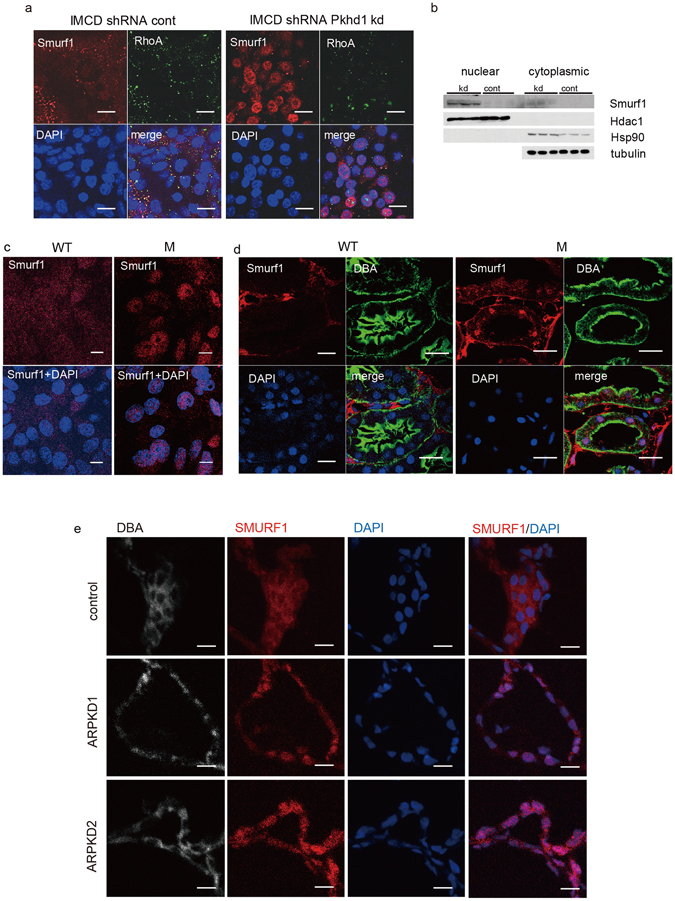
Smurf 1 is mis-localized in Pkhd1 mutants. (a) Immunolocalization of endogenous Smurf1 (red) and RhoA (green) in IMCD cells with stable expression of control shRNA vector and Pkhd1 shRNA. Smurf1 and RhoA co-localize in a subset of small vesicles in control cells with Smurf1 undetectable in the nucleus. In Pkhd1-silenced cells, Smurf1 localizes predominantly to the nucleus and is minimally detected in vesicles. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of shRNA vector control IMCD cells (cont) and shPkhd1 IMCD cells (kd) were immunoblotted as shown. Hdac1 and Hsp90 were used to show adequate separation of nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. Tubulin was used as a loading control. These results are consistent with the IF data in panel “a” and show significant enrichment of Smurf1 in the nuclear fraction of IMCD cells with shRNA-reduced Pkhd1 expression. The full-length blots of these cropped images are included in Supplementary Fig. S8. (c) Sub-cellular localization of Smurf1 (red) in primary cultures of collecting duct cells of wild type (WT) and Pkhd1 del3-4/del3-4 (M) mouse kidneys. Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. (d) Wild type (WT) and Pkhd1 del3-4/del3-4 mouse kidneys stained for Smurf1 (red), DBA (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20 μm. (e) Kidney specimens from human control (control) and two different ARPKD donors (ARPKD1, ARPKD2) stained for SMURF1 (red), DBA (grey), and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20μm.
