Figure 2.
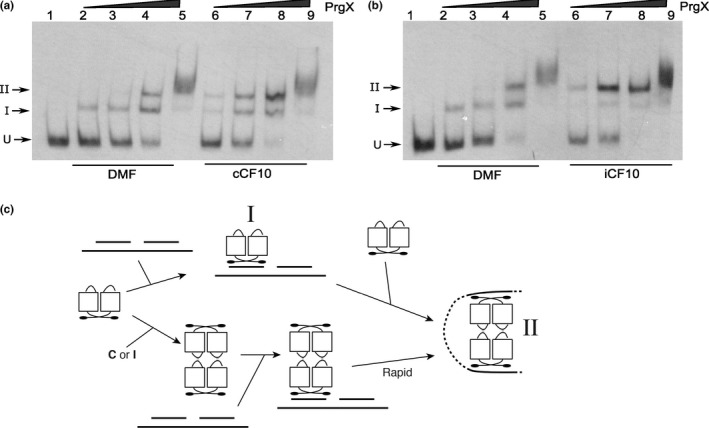
The effects of C and I on PrgX binding to XBS operator sites as determined by mobility gel shift assays. EMSA assays were performed using 8 fmol of digoxigenin‐labeled LT DNA probes with increasing amounts of PrgX protein. PrgX was preincubated for 5‐min at room temperature with 40 nmol L−1 of C (a) or I (b) before adding LT DNA. PrgX concentrations: lanes 2 and 6: 38 nmol L−1; lanes 3 and 7: 76 nmol L−1; lanes 4 and 8: 190 nmol L−1; lanes 5 and 9: 568 nmol L−1. (c) Cartoon showing the predicted products formed by binding PrgX to LT DNA. The upper part shows stepwise binding of PrgX dimers (Apo‐PrgX) to the XBS1 and XBS2 sites, followed by formation of a DNA loop via interaction between the two dimers, whereas the lower portion shows binding of a preformed tetramer (PrgX‐C or PrgX‐I) to XBS1, followed by very rapid forming of the looped structure. “I” and “II” indicate the shifted and supershifted protein/DNA complexes shown in (a) and (b)
