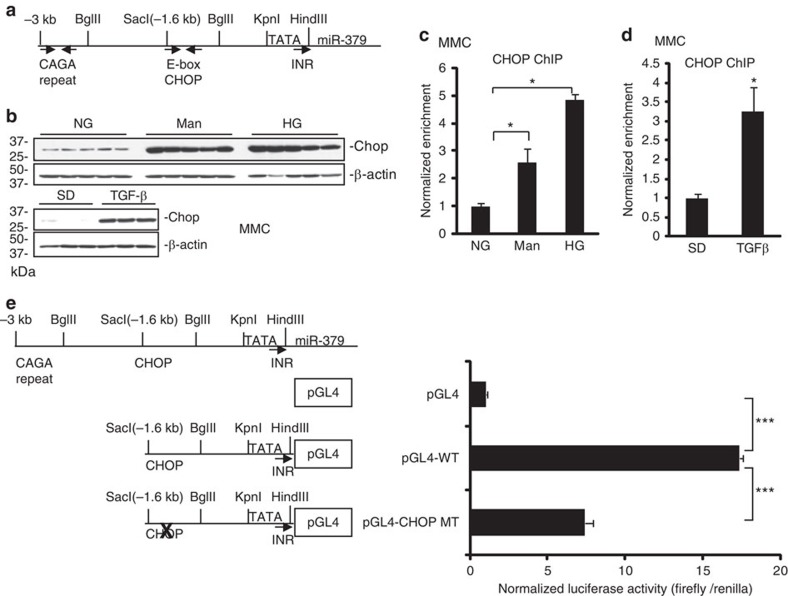
Figure 3. Regulatory role of CHOP.
(a) Genomic structure of the region upstream of miR-379. CAGA repeats (potential Smad-binding elements) were identified at ∼3 kb upstream of miR-379 and CHOP binding element and E-boxes were found close to a SacI restriction enzyme site at ∼1.6 kb upstream of miR-379. (b) Chop protein levels were increased in MMC treated with TGF-β1, HG or mannitol compared with respective controls. Wider (uncropped) scans are shown in Supplementary Fig. 38. (c,d) ChIP assays and ChIP-real-time PCRs. CHOP occupancy was enriched at the CHOP binding site in MMC treated with HG or mannitol (c) or TGF-β1 (d). Results are mean+s.e. in triplicate PCRs from three independent ChIP experiments. *P<0.05. (e) The upstream (−1.6 kb) region, or the same region with mutated CHOP binding site, was cloned into the luciferase reporter pGL4 and plasmids were transfected into MMC. The WT plasmid showed significantly higher luciferase activity than empty pGL4 and mutation of CHOP site (MT) significantly reduced promoter activity. Results are mean+s.e. from triplicate reads of four independent cultures. ***P<0.001.