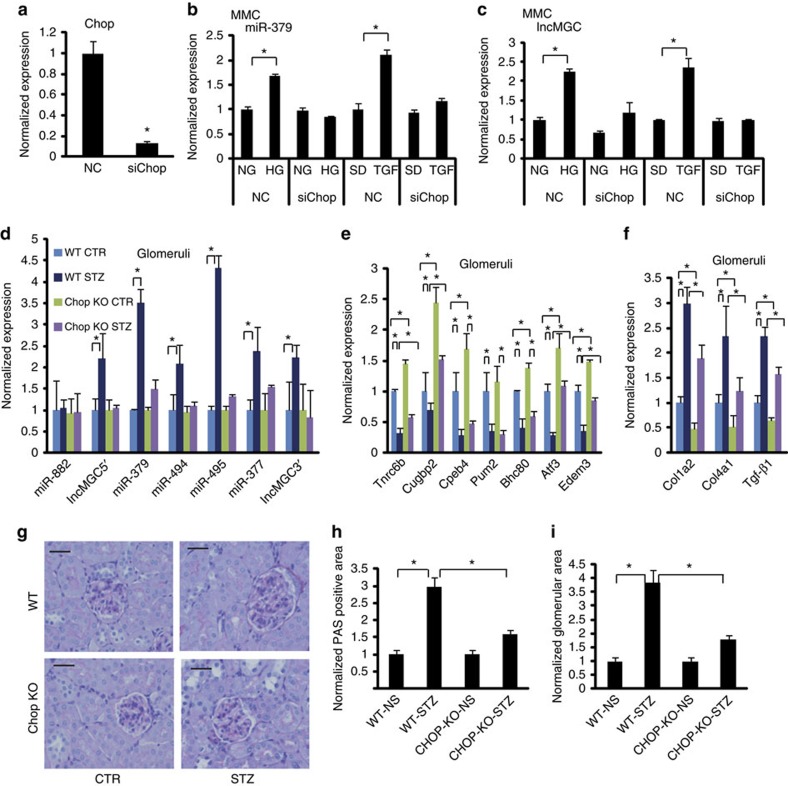
Figure 4. Regulatory role of CHOP (using siRNA and Chop-KO mice).
(a) Effects of Chop siRNA. Chop expression was significantly decreased by Chop siRNA in MMC. (b) Effects of Chop siRNA on the expression of miR-379. Chop siRNA inhibited TGF-β1 or HG mediated increase of miR-379 in MMC but had no effect on basal levels of miR-379. (c) Effects of Chop siRNA on the expression of lnc-MGC. Chop siRNA inhibited the induction of lnc-MGC in MMC treated with TGF-β1 or HG but had no effect on basal levels. Results are mean+s.e. in triplicate PCRs from three independent culture experiments, *P<0.05. (d) The miR-379 cluster miRNAs are not induced in the kidneys of diabetic Chop-KO mice. The increases of lnc-MGC, miR-379, miR-494, miR-495 and miR-377 noted in glomeruli from diabetic WT mice were not observed in glomeruli from diabetic Chop-KO mice (five mice in each group). (e) Decrease of potential targets of miR-379 cluster in glomeruli from diabetic WT mice and restoration of their expression in Chop-KO mice. (f) Increase of profibrotic gene expression in glomeruli from diabetic WT mice was attenuated in Chop-KO mice. (g–i) Glomerular hypertrophy and ECM accumulation were increased in WT diabetic mice and these were attenuated in diabetic Chop-KO mice. Scale bar, 20 μm. (h) PAS staining in glomeruli from WT and Chop-KO mice. PAS positive area (ECM accumulation). (i) glomerular area (hypertrophy). *P<0.05.