FIG 1.
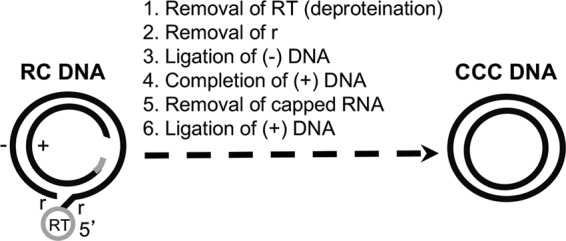
Biochemical reactions thought to be required for RC DNA conversion to CCC DNA. The structures of the HBV RC DNA found in mature intracellular nucleocapsids and extracellular complete virions and of the CCC DNA found in the host cell nucleus are shown schematically. The viral minus (−)-strand DNA and plus (+)-strand DNA are represented by black lines. RT, the viral RT protein covalently attached to the 5′ end of the minus strand of RC DNA; gray bar, the capped RNA oligomer attached to the 5′ end of the plus strand of RC DNA; r, a short (ca. 9-nt-long) terminal repeat at both ends of the minus strand of RC DNA. The gap in the inner circle represents the region in the incomplete plus strand of RC DNA that is yet to be synthesized during CCC DNA formation. Note that the numerals 1 through 6 refer only to the putative biochemical reactions required for RC DNA to CCC DNA conversion and do not necessarily reflect the order of events in this conversion.
