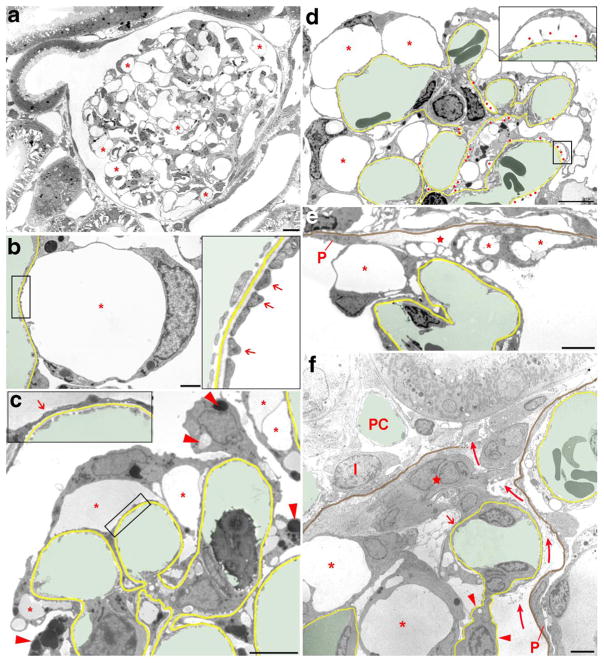
Fig. 1.
Transmission electron micrographs illustrating changes in podocyte morphology after puromycin aminonucleoside (PAN) treatment. In b–f, the GBM is highlighted in yellow, capillary lumens in green; in e and f, in addition, the parietal basement membrane (PBM) is shown in brown. a Overview of a whole glomerular profile showing that podocyte pseudocyst (asterisks) development concerns the entire glomerulus. Due to the many pseudocysts, the glomerular tuft appears hypertrophied. b Enlarged view of a pseudocyst (asterisk), the floor of which is still made up of interdigitating foot processes (arrows in the inset). c Glomerular area with pseudocysts of different sizes (asterisks), the floor of which mostly shows foot process effacement (arrow in the inset). Note the varying density of pseudocyst content likely reflecting different albumin concentrations. The accumulation of intracellular vesicles (lysosomes) of varying density is also visible in injured podocytes (arrowheads). d Advanced stage of damage with many pseudocysts (asterisks) and many areas of bare GBM where podocytes were detached (red dots). At those sites, in addition to large pseudocysts (asterisks), secondary small pseudocysts (enlarged in the inset) have developed that regularly communicate with the large pseudocysts (not encountered in this section). Accumulations of intracellular vesicles in podocytes are also seen. e Tuft adhesion to Bowman’s capsule. Podocytes with pseudocysts (asterisks) attach to the parietal epithelium (P) or parietal basement membrane (PBM; highlighted in brown). The integrity of the parietal epithelium is already lost; instead, fluid accumulation is seen (star). Outside the PBM loose connective tissue has settled. F: Advanced tuft adhesion to Bowman’s capsule accompanied with a break of the PBM and a displacement of the parietal epithelial cells (P) leading to an open connection between Bowman’s and the interstital spaces (curved arrows). A peripheral capillary loop still covered by “effaced” podocyte portions (arrow) is attached to a group of (most likely) parietal cells (star); the mesangial stalk of this loop is deprived of podocytes (arrowheads). Other podocytes with pseudocysts (asterisks) adhere to the adhesion. I, interstitial cell; PC, peritubular capillary. Images of a–d were taken 4 days, images of e and f 8 days after PAN treatment. Scale bars = 10 μm (a), 5 μm (d–f), and 2 μm (b, c)