Figure 2. Key Figure. Integrating Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Annotation into the Genome-wide Association Study (GWAS) Pipeline.
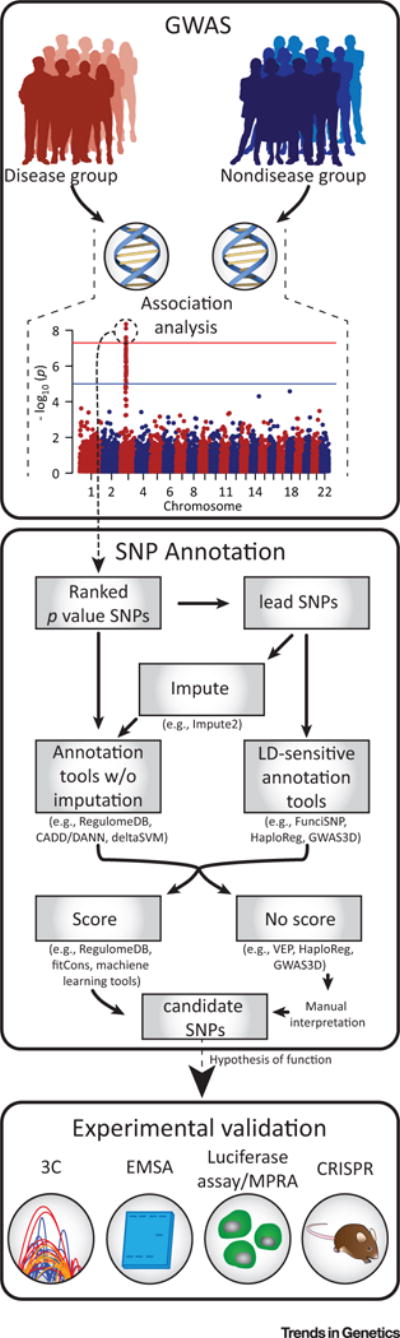
Following GWAS analysis, lead SNPs implicated as important in disease risk can be passed to an SNP annotation tool. Annotation tools sensitive to linkage disequilibrium (LD) regions, or who make predictions covering genomic regions can be used directly, while those tools without imputation methods must first be put through an imputation program to make predictions for all SNPs in a region of LD. Once a SNP annotation tool has been implemented, the resulting scores or functional annotations can be used to prioritize candidate SNPs for further experimental validation following generation of a hypothesis of function. Abbreviations: 3C, chromosome conformation capture; CADD, combined annotation-dependent depletion; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; DANN, deleterious annotation of genetic variants using neural networks; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assay; FunciSNP, Functional Identification of SNPs; MPRA, massively parallel reporter assay; VEP, Variant Effect Predictor.
