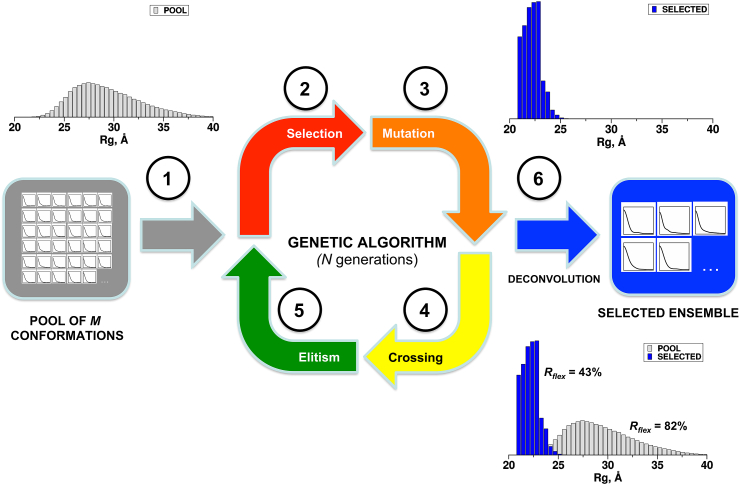
Fig. 3.
Workflow of the Ensemble Optimization Method (EOM). Overall scheme of EOM. The conformational space of the system is explored through the generation of a random pool with SAXS curves computed for each conformer (1). Sub-ensembles of these curves are randomly selected to form “chromosomes”(2) and these chromosomes are subjected to a series of mutation(3) and crossing steps (4). The mutation stage allows swapping/replacement of curves within the current set of chromosomes and also with curves randomly selected from the pool. The crossing stage randomly selects two chromosomes from the current set and swaps a minimum of two curves to generate a new chromosome. The chromosomes that provide the best fit the experimental scattering data are evaluated at the elitism stage (5) and passed to the next generation in an iterative process. The process is repeated until the deconvolution stage (6), where parameters are averaged and the final size-distributions (eg. Rg, Dmax) and metrics (Rflex, Rσ) of selected ensembles constructed and compared with that of the initial pool.