Fig. 1.—
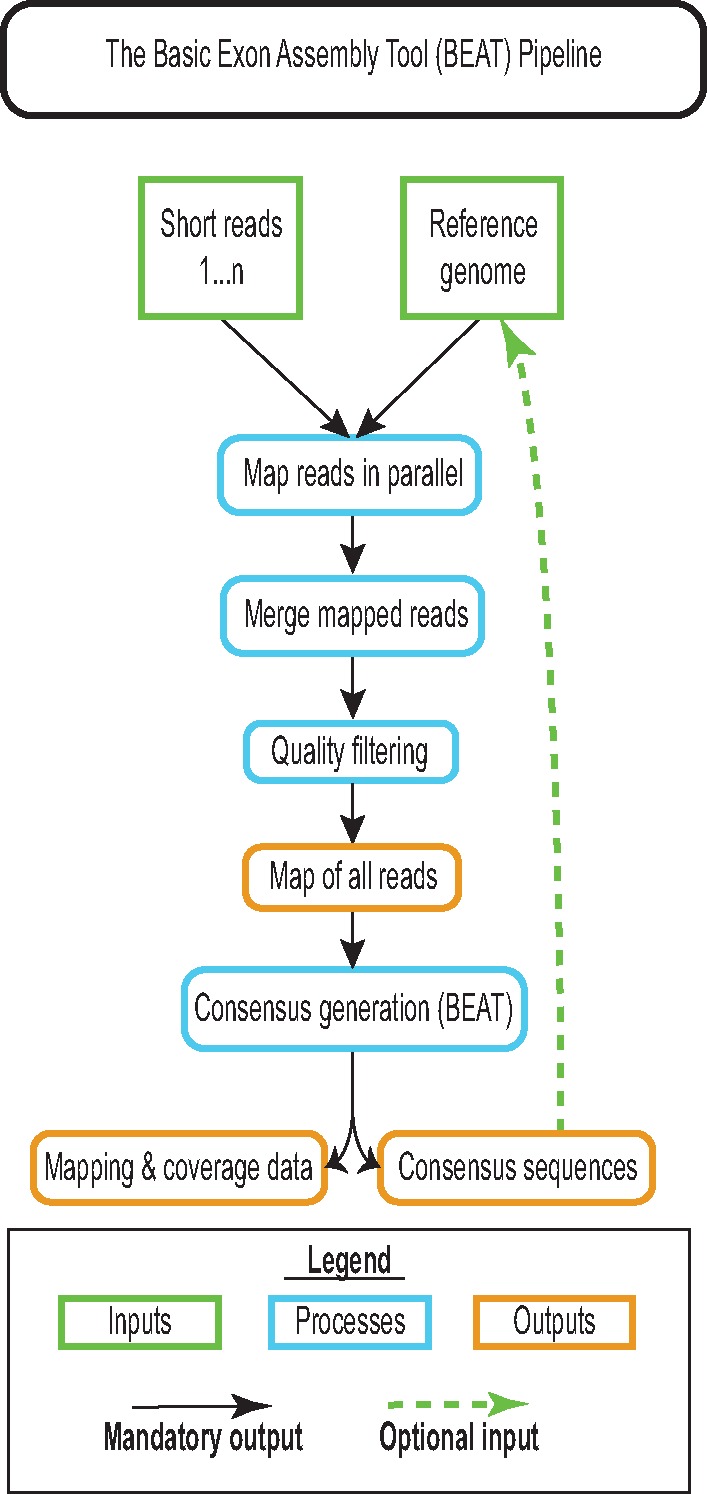
The basic workflow used by BEAT when assembling a single query sequence from a short read data set. BEAT maps all short-reads provided to a reference genome in parallel, removes low-quality and duplicate reads, then merges the mapped files to produce a map of all reads in the data set. Mapped reads are then scanned nucleotide-by-nucleotide against the reference, and a call for each position is generated by taking the quality-weighted median call of all mapping reads at positions with a depth of coverage >2. To avoid genotyping error when generating consensus sequences for loci of interest from a distantly related reference, BEAT should be run twice, with the second iteration using the consensus generated by the first as its reference.
