Figure 1. Domains and structure of the AMPK complex.
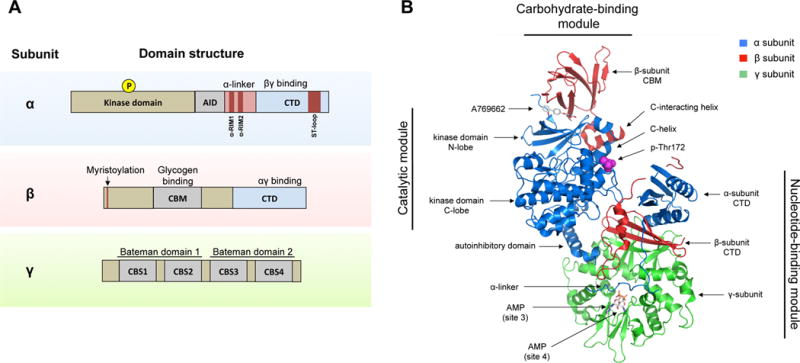
A) AMPK exists as a trimeric complex consisting of a catalytic subunit (α) and two regulatory subunits (β and γ). The main protein domains are shown. Abbreviations: AID (autoinhibitory domain), CTD (C-terminus domain), NTD (N-terminus domain), CBM (carbohydrate-binding module), CBS (cystathionine β-synthase repeats), RIM (regulatory-subunit-interacting motif), ST-loop (serine/threonine enriched loop).
B) The crystal structure of the AMPK α2β1γ1 trimeric complex is shown. Major structural domains are indicated. The structure shows the activator A769662 bound to a pocket formed by the interface between the kinase domain and the CBM. Also shown are two AMP molecules bound to site 3 and site 4, respectively, and phospho-Thr172. The ST-loop in the α-subunit and the myristoylation site in the β-subunit are not resolved in this structure. Structure sourced and adapted from PDB file 4CFF, using PyMOL software.
