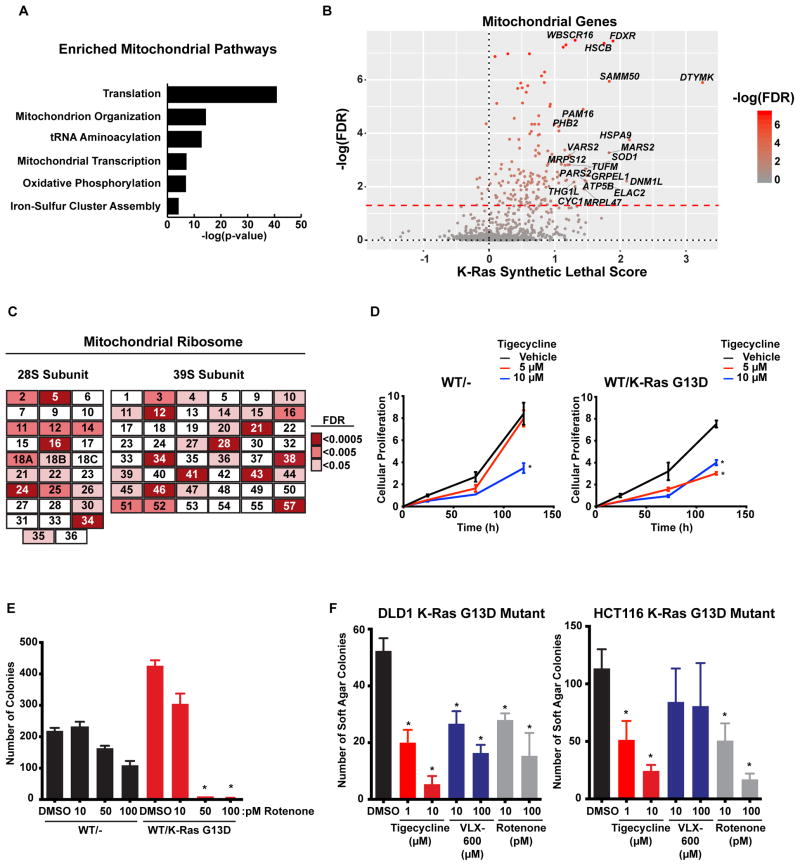
Figure 2. Mitochondrial genes and pathways are synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras.
A. Pathways enriched among the mitochondrial genes that are putative synthetic lethal. B. Mitochondrial genes identified in the DLD1 screen. C. Depletion of the mitochondrial ribosome is synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras. Components of the mitoribosome from the DLD1 screen and their associated FDR corrected p-values. D. Inhibition of mitochondrial translation is more toxic to K-Ras mutant cells. Isogenic DLD1 cells were treated with the mitochondrial translation inhibitor tigecycline and proliferation was measured. E. Inhibition of complex I of the respiratory chain is more toxic to K-Ras mutant cells. Colony formation of isogenic HCT116 cells treated with the complex I inhibitor rotenone. F. Inhibition of either the mitoribosome or complex I reduces the anchorage-independent growth of K-Ras mutant cells. Soft agar colony formation was measured in K-Ras mutant cells treated with the mitochondrial inhibitors. For all panels * denotes p<0.05. All cellular growth and allograft data are expressed as the average ± SEM.