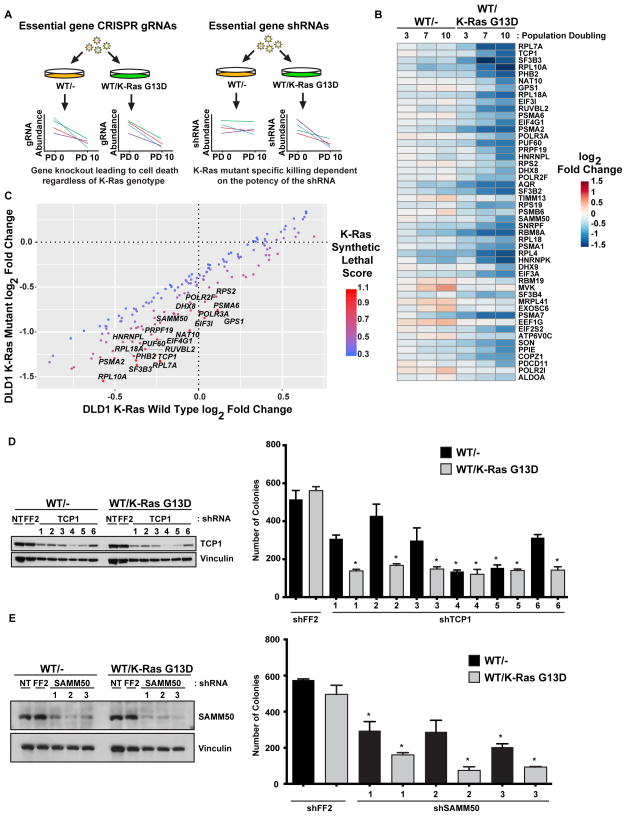
Figure 3. An shRNA screen targeting essential genes identifies additional synthetic lethal partners with mutant K-Ras.
A. shRNA but not CRISPR-based screens can identify essential genes as synthetic lethal partners. Essential genes are universally lost in CRISPR-based screens while shRNA-based screens can identify whether the reduced function of essential genes can be synthetic lethal. B. An shRNA screen to identify essential genes that are synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras in isogenic DLD1 cells. Heat map showing the log2 fold change at PD3, PD7, and PD10 of essential genes that are putative synthetic lethal partners of mutant K-Ras. C. Essential genes that are synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras. Labeled genes are more strongly depleted in K-Ras mutant cells. D. Knockdown of CCT1/TCP1 is synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras. Colony formation of isogenic DLD1 cells expressing tet-inducible shRNAs for TCP1. E. Knockdown of SAMM50 is synthetic lethal with mutant K-Ras. Colony formation of isogenic DLD1 cells expressing constitutively expressed shRNAs for SAMM50. For all panels * denotes p<0.05. All cellular growth and allograft data are expressed as the average ± SEM. For screen sequencing data and analysis, see Supplemental Table S6.