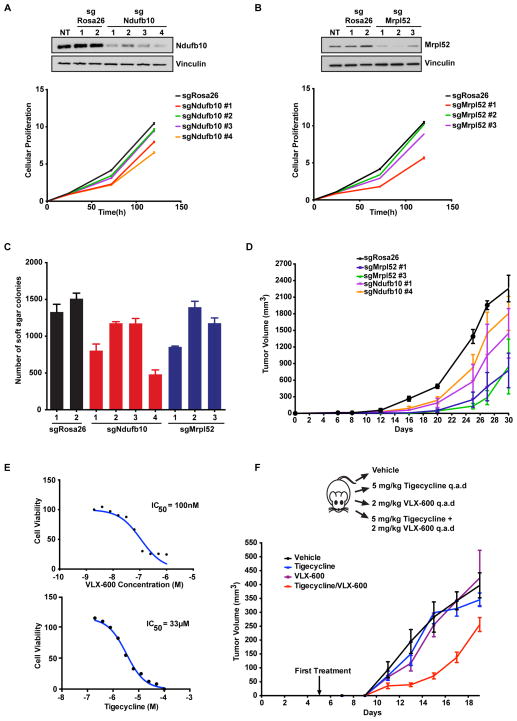
Figure 5. Knockout of synthetic lethal genes or inhibition of complex I and the mitoribosome reduces K-Ras mutant cell growth in vivo.
A. Knockout of Ndufb10 reduces the proliferation of CT26 tumor cells. Cas9 and gRNAs targeting either control Rosa26 or Ndufb10 were expressed in CT26 cells and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins (above) and measured for proliferation (below). NT is non-treated. B. Mutation of Mrpl52 reduces the proliferation of CT26 tumor cells. Cas9 and gRNAs targeting either control Rosa26 or Mrpl52 were expressed in CT26 cells and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins (above) and measured for proliferation (below). NT is non-treated. C. Mutation of either Ndufb10 or Mrpl52 reduces the anchorage-independent growth of CT26 tumor cells in soft agar. Cells from A and B were tested for anchorage independent growth in soft agar and colony number was quantified. D. Mutation of either Ndufb10 or Mrpl52 reduces the in vivo tumor growth of CT26 tumor cells. CT26 cells expressing Cas9 and control Rosa26 gRNA or gRNAs targeting either Ndufb10 or Mrpl52 were subcutaneously injected as allografts in BALB/c mice and tumor growth was measured over time. E. CT26 cells are sensitive to complex I inhibition by VLX-600 and mitoribosome inhibition by tigecycline. CT26 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of VLX-600 or tigecycline to determine sensitivity to oxidative phosphorylation or mitochondrial translation inhibition, respectively. Cell viability was measured 72h after drug treatment and IC50 values for each compound were determined. F. Combined mitochondrial inhibition by VLX-600 and tigecycline reduces tumor growth. CT26 subcutaneous allografts were treated with the indicated inhibitors/concentrations and tumor growth was monitored. All cellular growth and allograft data are expressed as the average ± SEM.