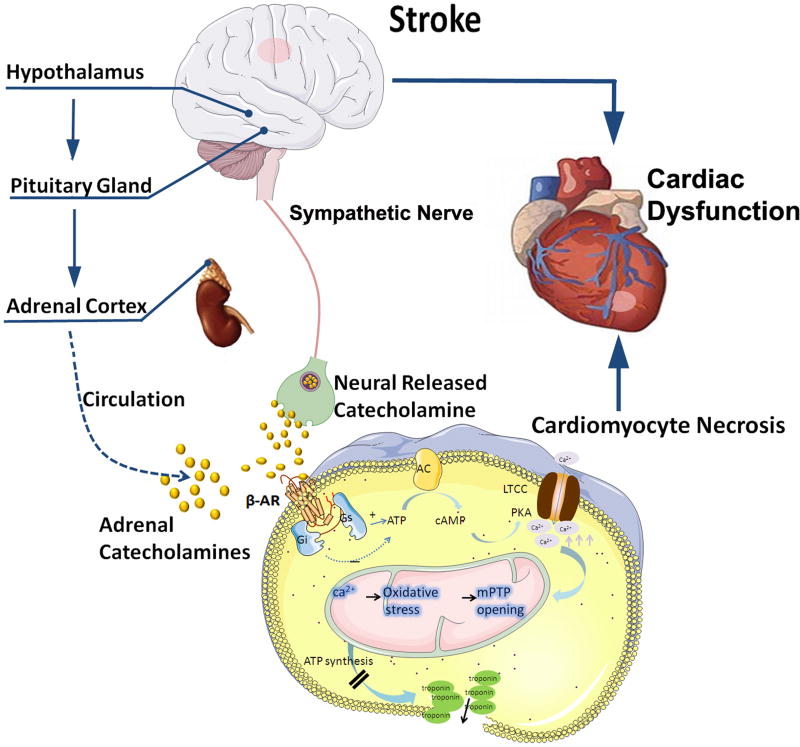
Figure 2. The HPA axis, catecholamine surge and sympathetic and parasympathetic regulation mediate cardiac dysfunction after stroke.
Catecholamines act on β receptors, β receptors couple to the stimulatory G protein (Gs) and activate adenylyl cyclase (AC), and increase cytosolic cAMP. cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits of protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates sarcolemmal L-type Ca2+ channels (LTCC) and sarcoplasmic phospholamban, which over loads mitochondria. Mitochondrial Ca2+ overload triggers oxidative stress, and the subsequent opening of their inner membrane permeability transition pore with ensuing osmotic swelling and loss of ATP synthesis, leads to myocardial cell death.