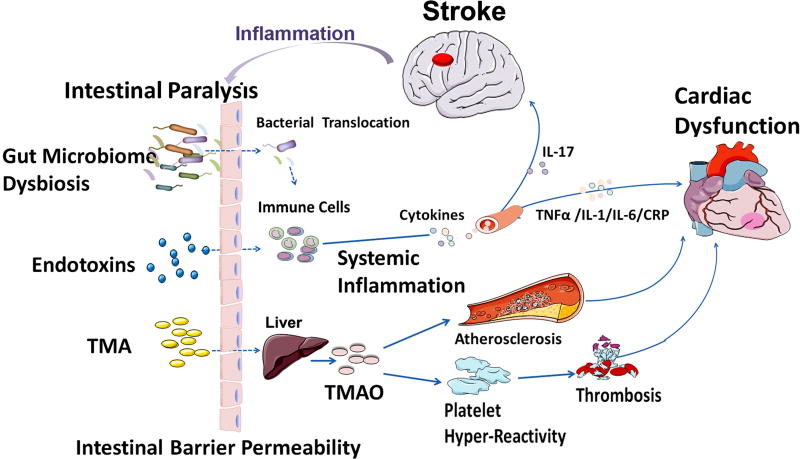
Figure 4. The brain-gut axis and gut-heart axis may mediate cardiac damage after stroke.
Stroke increases intestinal barrier permeability, enabling bacterial and endotoxin translocation to bloodstream inducing inflammatory responses and proinflammatory cytokine production. Cytokine production can trigger inflammation, fibrosis and microvascular and myocardial dysfunction. TMAO is the hepatic oxidation product of the microbial metabolite TMA. TMAO promotes the development of hyper responsive platelet phenotype and enhances elevating the risk for heart failure and/or heart attack.