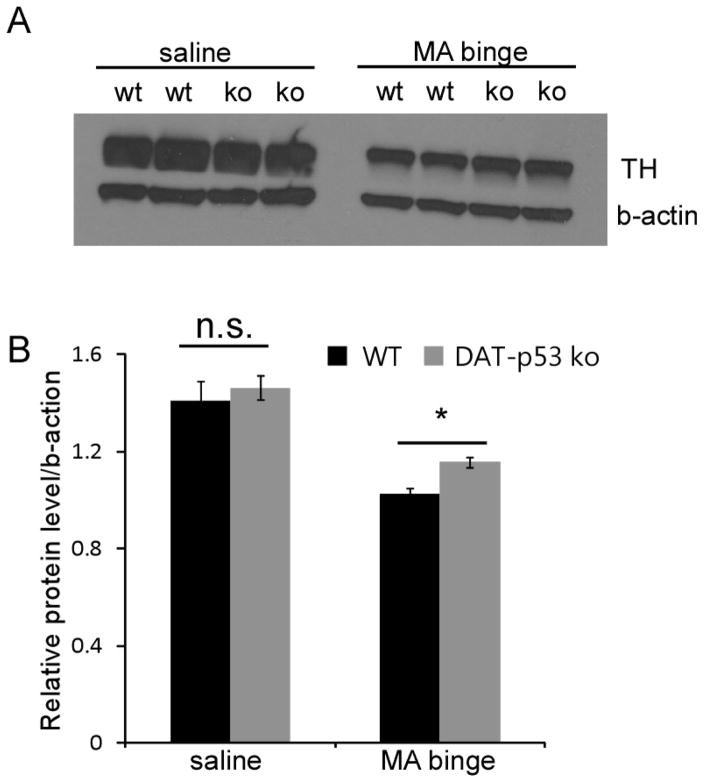
Fig 3.
p53 gene deletion in dopaminergic neurons results in moderate protection of TH protein levels in striatum after MA binge exposure in DAT-p53KO mice. Brain tissue (striatum) was collected at 72 hours after MA binge challenge. Protein levels of TH in striatum (A) were examined by Western blot analysis. Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Quantification of data in (A) shows that MA binge exposure leads to a decrease in TH protein levels in striatum in WT animals, and this decrease in TH protein level is attenuated in DA-p53KO mice. Data are mean ± SEM. * p<0.05 DAT-p53KO vs. -WT mice after MA binge exposure. The data was analyzed by two-way ANOVA, with Newman–Keuls post hoc tests. n=4–6 for each group.