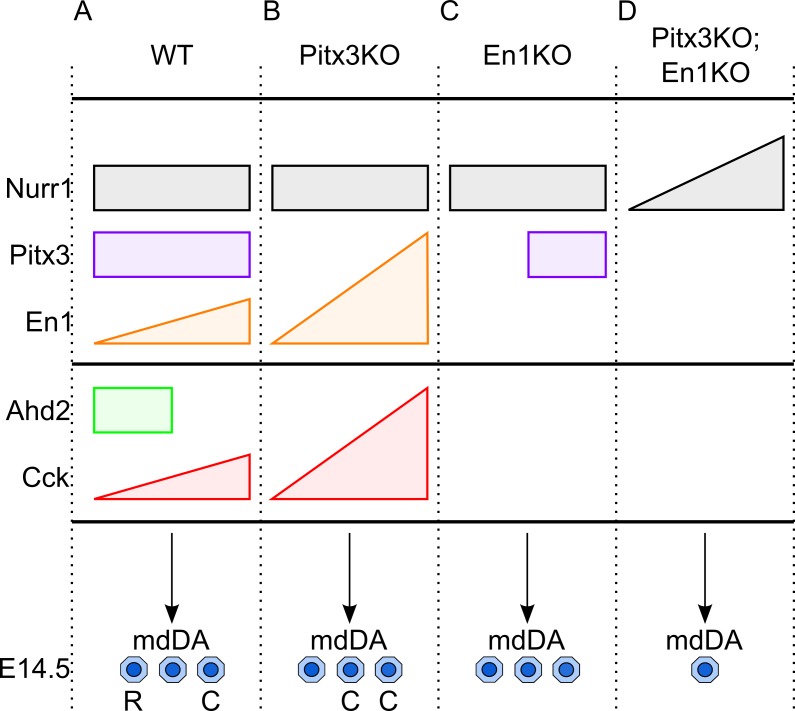
Fig 7. Schematic representation of roles of En1 and Pitx3 in the programming of the rostral-caudal identity of mdDA neurons.
(A) In wild-type midbrain Nurr1 initiates the development of mdDA differentiation, Pitx3 promotes Ahd2 expression and represses En1 in rostral midbrain, whilst En1 promotes Pitx3 and Cck expression. The mdDA neuronal pool includes rostral-coded and caudal-coded neurons. (B) In Pitx3-ablated animals Nurr1 initiates the development of mdDA differentiation, though Ahd2 expression is lost, and the inhibition of Pitx3 on En1 is lifted, thus En1 and subsequently Cck are up-regulated. The mdDA neuronal pool includes only caudal-coded neurons. (C) In En1-ablated animals Nurr1 initiates the differentiation of mdDA progenitors, though Cck expression is lost, and Pitx3 expression in the rostral midbrain is not initiated, thus Ahd2 expression is lost as well. The mdDA neuronal pool includes only non-coded neurons. (D) In double En1KO;Pitx3GFP/GFP animals elevated levels Nurr1 promotes the differentiation of mdDA progenitors, though Cck and Ahd2 are lost.