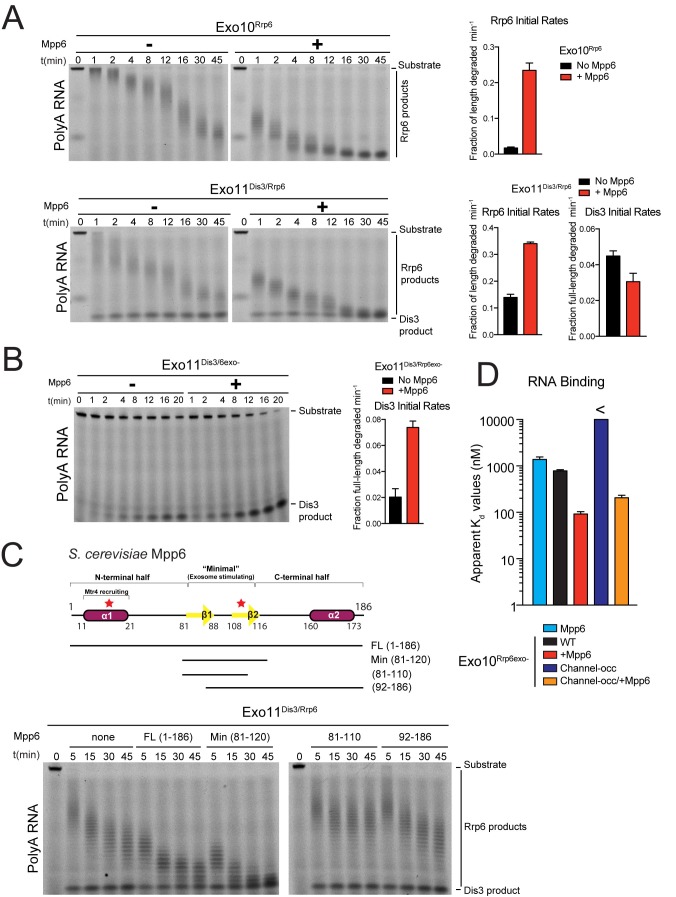
Figure 1. Mpp6 stimulates the nuclear RNA exosome and binds RNA.
(A) Mpp6 stimulates Rrp6 activities when degrading 5’ fluorescein-labeled 49 nt polyA in 10- (top) and 11- subunit exosomes (bottom). Relative positions of RNA substrate, Rrp6 products and the Dis3 product are indicated to the right of gels in panels A, B, and C. Quantitation of initial rates shown to the right of representative gels. For Rrp6 initial rates, the median length of Rrp6 products was determined at the earliest time points and used to calculate initial rates using the equation (1 – (median product length/substrate length)/min) to yield a fraction of length degraded per minute. For Dis3, initial rates were determined by calculating the fraction of full-length substrate degraded based on the accumulation of 4–5 nt product. For the lower gel, Dis3 and Rrp6 initial rates were determined at the earliest time points where distributive products of Rrp6 are easily distinguished/separated from the 4–5 nt processive products of Dis3. (B) Dis3 exoribonuclease activity can be stimulated on 5’ fluorescein-labeled 49 nt polyA in 11-subunit exosomes if Rrp6 is present but catalytically inert. (C) Top: Predicted domain structure of S. cerevisiae Mpp6. Calculated with Jpred (Cole et al., 2008). Previously identified conserved regions (Milligan et al., 2008) are marked with red stars, with Mtr4 recruiting and exosome stimulating domains as described in this work labeled. Below: a minimal fragment of Mpp6 (residues 81 to 120) is necessary and sufficient to stimulate Rrp6 activity in Exo11Dis3/Rrp6. Representative decay assays of Exo11Dis3/Rrp6 on 5’ fluorescein-labeled polyA 49 nt RNA with different Mpp6 constructs added in 2-fold molar excess. (D) Mpp6 enhances RNA binding of Rrp6-containing exosomes on polyA RNA, and alleviates binding defects caused by Exo9 channel occlusions. Fluorescence polarization of Mpp6 and Exo10Rrp6exo- with or without PH-like ring occlusions in the lower half of the Exo9 channel, with binding to 5’ fluorescein-labeled polyA 37 nt RNA. Bar graphs and error bars in panels A, B, and D are the result of triplicate experiments with error bars indicating plus or minus one standard deviation.