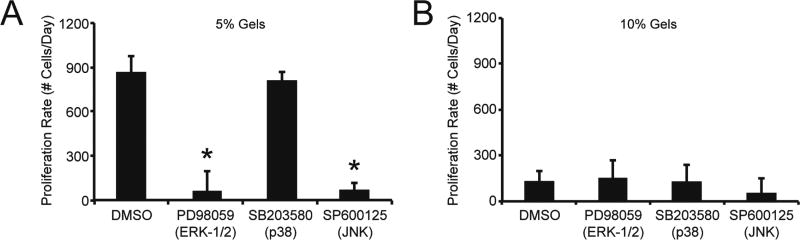
Fig. 7. AF proliferation rate in 5% and 10% hydrogels with MAPK inhibitors.
Following encapsulation in (A) 5% and (B) 10% hydrogels, AFs were treated with ERK-1/2 pathway inhibitor PD98059 (10 µmol/L), the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (10 µmol/L), or the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 µmol/L). (A) In 5% hydrogels, AF proliferation rate was significantly decreased when gels were treated with JNK inhibitor SP600125 or the ERK pathway inhibitor PD98059. However, AF proliferation rate in 5% gels was not altered when treated with the p38 inhibitor SB203580. (B) In 10% hydrogels, proliferation rate was not altered when ERK-1/2, p38, or JNK pathways were inhibited. * represents significance from DMSO-treated control gels (p<0.05 by ANOVA with Tukey HSD). N=3.