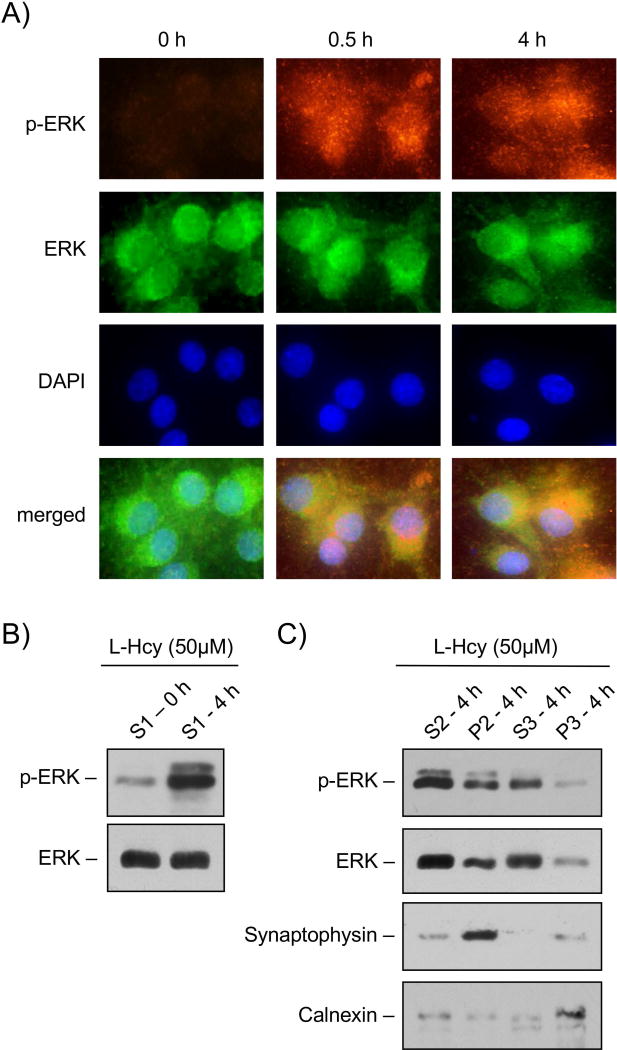
FIGURE 5. Subcellular localization of phosphorylated ERK MAPK in neurons treated with homocysteine.
(A) Immunocytochemical analysis illustrating the cytoplasmic and nuclear distribution of p-ERK (red) and ERK (green) MAPK in neurons following 50 μM of L-homocysteine (L-Hcy) treatment for 0 min, 30 min (0.5 h) or 4 h. The cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (B) Immunoblot analysis of the S1 fraction (supernatant following centrifugation of cell homogenate at 1,000 × g) obtained from neurons treated with L-homocysteine (50 μM) for 0 or 4 h using anti-p-ERK (upper panel) or anti-ERK (lower panel) antibody. (C) Sub-cellular distribution of phosphorylated ERK MAPK in neurons treated with L-homocysteine (50 μM, 4 h) was analyzed by immunoblot analysis of biochemical fractions with anti-p-ERK (panel 1) or anti-ERK (panel 2) antibody. Purity of the fractions was also evaluated by immunoblot analysis with anti-synaptophysin (panel 3) and anti-calnexin (panel 4) antibodies. The biochemical fractions evaluated are S2 (supernatant following centrifugation of S1 fraction at 10,000 × g), P2 (pellet comprising of crude synaptosomal membrane proteins following centrifugation of S1 fraction at 10,000 × g), S3 (final cytosolic fraction obtained following centrifugation of S2 fraction at 1,65,000 × g) and P3 (pellet comprising mainly of light membrane proteins obtained following centrifugation of S2 fraction at 1,65,000 × g).