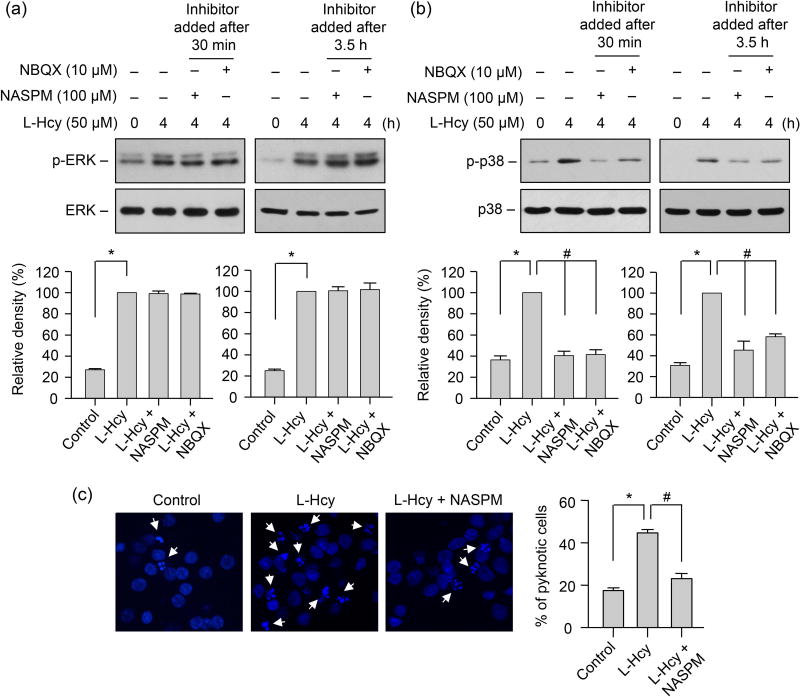
FIGURE 7. Role of GluA2-lacking AMPAR activity in homocysteine-mediated phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and subsequent neuronal death.
(A, B) Neuronal cultures were treated with 50 μM of L-homocysteine (L-Hcy) for 4 h and NASPM (100 μM) or NBQX (10 μM) was added 30 min or 3.5 h after the onset of homocysteine treatment. Phosphorylation of ERK MAPK and p38 MAPKs was analyzed using (A) anti-p-ERK antibody or (B) anti-p-p38 antibody (upper panels). Total pERK MAPK or p38 MAPK was analyzed by reprobing the blots with either (A) anti-ERK or (B) anti-p38 antibody (lower panels). Quantitative analysis of phosphorylated ERK and p38 MAPKs is represented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). *p < 0.001 from 0 min time point or control; #p < 0.001 from 4 h homocysteine treatment. (C) Neurons were treated with L-homocysteine (50 μM, 18 h) in the absence or presence of NASPM (100 μM, added 30 min after the onset of L-homocysteine treatment) and then stained with Hoechst 33342, 18 h later. Representative photomicrographs show pyknotic DNA stained with Hoechst 33342 (indicated with arrows). Percentage of neurons with pyknotic nuclei is represented as mean ± SEM (n = 1500 cells/condition from 4 experiments). *p < 0.001 from control; #p < 0.05 from 18 h homocysteine treatment.