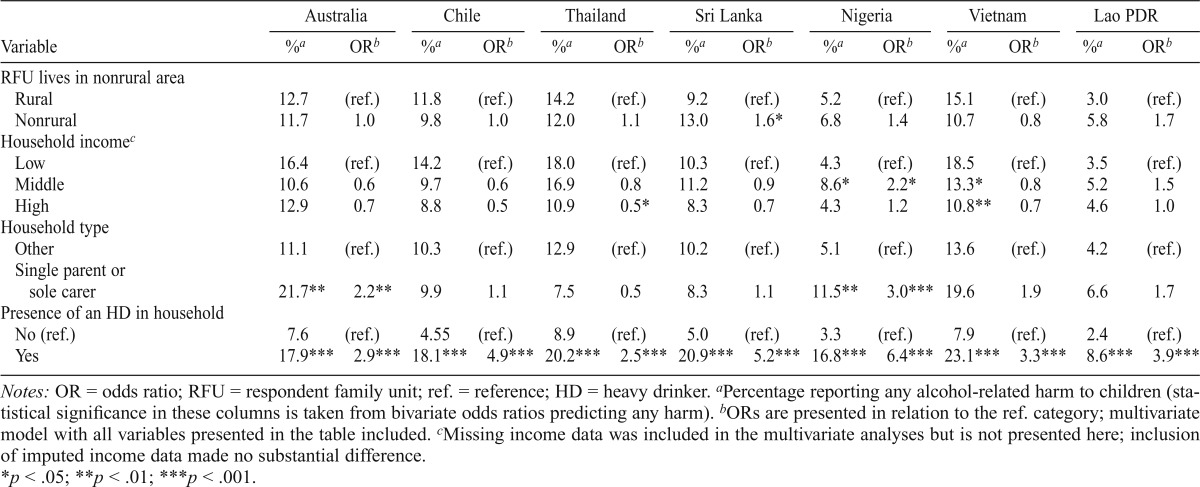
Table 4.
Logistic regression models predicting reporting of alcohol-related harm to children
| Australia |
Chile |
Thailand |
Sri Lanka |
Nigeria |
Vietnam |
Lao PDR |
||||||||
| Variable | %a | ORb | %a | ORb | %a | ORb | %a | ORb | %a | ORb | %a | ORb | %a | ORb |
| RFU lives in nonrural area | ||||||||||||||
| Rural | 12.7 | (ref.) | 11.8 | (ref.) | 14.2 | (ref.) | 9.2 | (ref.) | 5.2 | (ref.) | 15.1 | (ref.) | 3.0 | (ref.) |
| Nonrural | 11.7 | 1.0 | 9.8 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 1.1 | 13.0 | 1.6* | 6.8 | 1.4 | 10.7 | 0.8 | 5.8 | 1.7 |
| Household incomec | ||||||||||||||
| Low | 16.4 | (ref.) | 14.2 | (ref.) | 18.0 | (ref.) | 10.3 | (ref.) | 4.3 | (ref.) | 18.5 | (ref.) | 3.5 | (ref.) |
| Middle | 10.6 | 0.6 | 9.7 | 0.6 | 16.9 | 0.8 | 11.2 | 0.9 | 8.6* | 2.2* | 13.3* | 0.8 | 5.2 | 1.5 |
| High | 12.9 | 0.7 | 8.8 | 0.5 | 10.9 | 0.5* | 8.3 | 0.7 | 4.3 | 1.2 | 10.8** | 0.7 | 4.6 | 1.0 |
| Household type | ||||||||||||||
| Other | 11.1 | (ref.) | 10.3 | (ref.) | 12.9 | (ref.) | 10.2 | (ref.) | 5.1 | (ref.) | 13.6 | (ref.) | 4.2 | (ref.) |
| Single parent or sole carer | 21.7** | 2.2** | 9.9 | 1.1 | 7.5 | 0.5 | 8.3 | 1.1 | 11.5** | 3.0*** | 19.6 | 1.9 | 6.6 | 1.7 |
| Presence of an HD in household | ||||||||||||||
| No (ref.) | 7.6 | (ref.) | 4.55 | (ref.) | 8.9 | (ref.) | 5.0 | (ref.) | 3.3 | (ref.) | 7.9 | (ref.) | 2.4 | (ref.) |
| Yes | 17.9*** | 2.9*** | 18.1*** | 4.9*** | 20.2*** | 2.5*** | 20.9*** | 5.2*** | 16.8*** | 6.4*** | 23.1*** | 3.3*** | 8.6*** | 3.9*** |
Notes: OR = odds ratio; RFU = respondent family unit; ref. = reference; HD = heavy drinker.
Percentage reporting any alcohol-related harm to children (statistical significance in these columns is taken from bivariate odds ratios predicting any harm).
ORs are presented in relation to the ref. category; multivariate model with all variables presented in the table included.
Missing income data was included in the multivariate analyses but is not presented here; inclusion of imputed income data made no substantial difference.
p < .05;
p < .01;
p < .001.