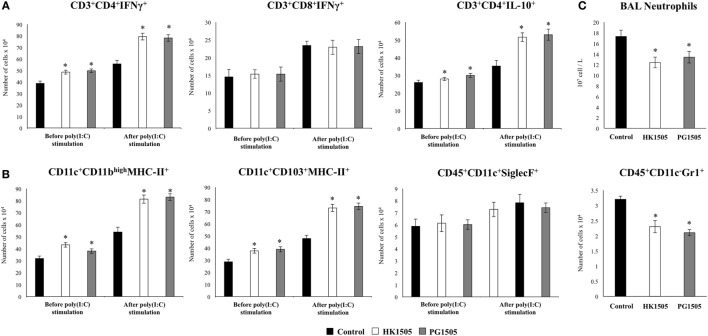
Figure 3.
Effect of non-viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505 (HK1505) and its peptidoglycan (PG1505) on respiratory immune cell populations before and after the nasal administration of the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern poly(I:C). Infant mice were nasally primed with HK1505 or PG1505 during two consecutive days and then challenged with three once-daily doses of poly(I:C). Non-treated infant mice challenged with poly(I:C) were used as controls. Before and 2 days after poly(I:C) administration, the numbers of lung T cells (A) including CD3+CD4+IFN-γ+, CD3+CD4+IL-10+, and CD3+CD8+IFN-γ+ T lymphocytes, as well as antigen presenting cells (B) including MHC-II+CD11c+CD11blowCD103+ and MHC-II+CD11c+CD11bhighCD103− dendritic cells, and CD45+CD11c+SiglecF+ alveolar macrophages were determined by flow cytometry. In addition, bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) neutrophils and lung CD45+CD11c−Gr1+ cells (C) were determined. The results represent data from three independent experiments. Significant differences between treated and control groups, *P < 0.05.