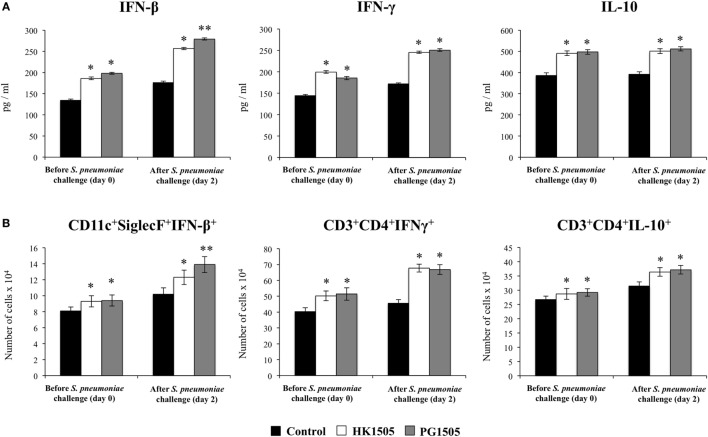
Figure 6.
Effect of non-viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505 (HK1505) and its peptidoglycan (PG1505) on the respiratory immune response to secondary pneumococcal pneumonia after the nasal administration of the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern poly(I:C). Infant mice were nasally primed with HK1505 or PG1505 during two consecutive days, challenged with three once-daily doses of poly(I:C) and, infected with two different doses of Streptococcus pneumoniae 5 days after the last poly(I:C) administration. Non-treated infant mice stimulated with poly(I:C) and challenged with S. pneumoniae were used as controls. The levels of interferon (IFN)-β, IFN-γ, and interleukin (IL)-10 in bronchoalveolar lavages (A), as well as the numbers of lung CD3+CD4+IFN-γ+, and CD3+CD4+IL-10+ T cells and CD45+CD11c+SiglecF+ alveolar macrophages (B) were determined before (day 0) and after (day 2) pneumococcal challenge. The results represent data from three independent experiments. Significant differences between treated and control groups, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.