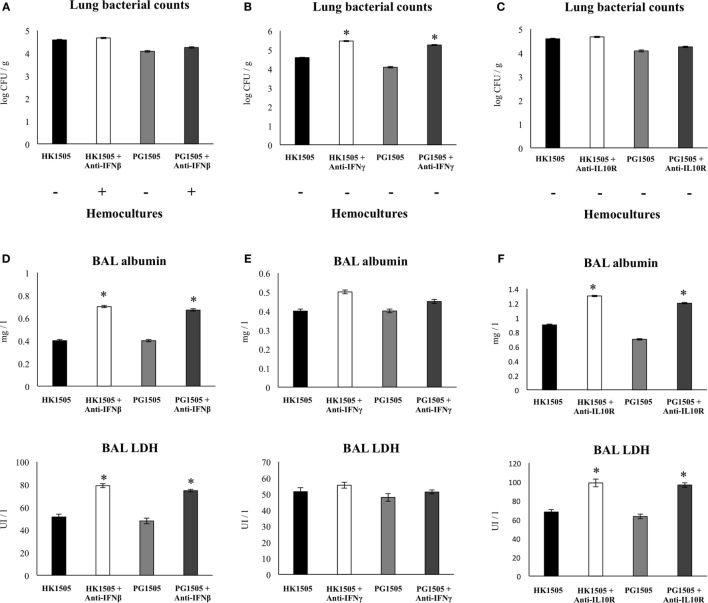
Figure 7.
Role of interferon (IFN)-β, IFN-γ, and interleukin (IL)-10 in the immunomodulatory effect of non-viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505 (HK1505) and its peptidoglycan (PG1505) on the resistance to secondary pneumococcal pneumonia after the nasal administration of the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern poly(I:C). Infant mice were nasally primed with HK1505 or PG1505 during two consecutive days, and then challenged with three once-daily doses of poly(I:C). On days 2 and 4 after poly(I:C) challenge, mice were nasally treated anti-IFN-β, anti-IFN-γ, or anti-IL-10 receptor (IL-10R) blocking antibodies. Control HK1505 and PG1505 received isotype control antibodies. Twelve hours later mice were challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Lung bacterial cells counts and hemocultures (A–C), as well as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity and albumin concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) (D–F) were determined on day 2 post-pneumococcal challenge. The results represent data from three independent experiments. Significant differences between treated and control groups, *P < 0.05.