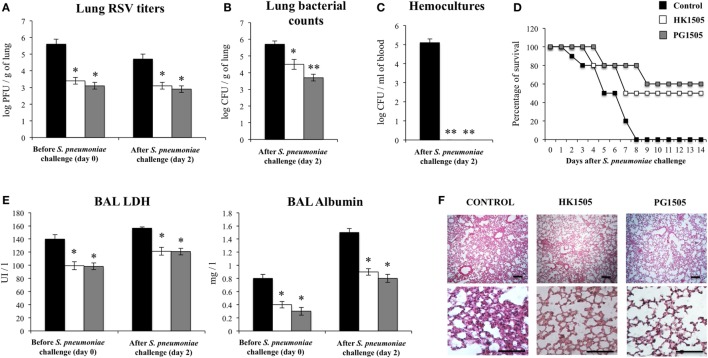
Figure 8.
Effect of non-viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505 (HK1505) and its peptidoglycan (PG1505) on the resistance to secondary pneumococcal pneumonia after the primary infection with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). Infant mice were nasally primed with HK1505 or PG1505 during two consecutive days, challenged with RSV and, infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae 5 days after the viral infection. Non-treated infant mice infected with RSV and challenged with S. pneumoniae were used as controls. Lung RSV titers (A), lung bacterial cells counts (B), hemocultures (C), survival (D), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, and albumin concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) (E), and lung histopathological examination (F) were determined on day 2 post-pneumococcal challenge. Scale bar = 100 μm. The results represent data from three independent experiments. Significant differences between treated and control groups, **P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.