Figure 2.
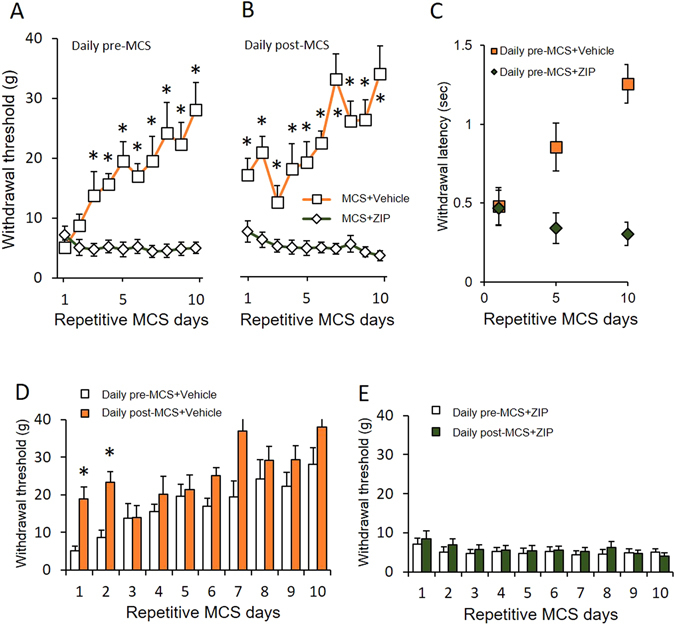
ZIP effects on the MCS-treated neuropathic pain. (A) Comparison of ZIP and vehicle injections with pre-MCS in neuropathic rats. Mechanical allodynia developed in the MCS with vehicle injection group. However, ZIP injection group did not show significant changes. (B) Comparison of ZIP and vehicle injections with post-MCS in neuropathic rats. Vehicle injection did not influence the effects of MCS. However, the effects of MCS were completely blocked by ZIP injections in the ACC. (C) Comparison of the withdrawal latency changes between MCS + Vehicle and MCS + ZIP injection rats. Latency of vehicle-injected rats was gradually elevated after repetitive MCS (Daily pre-MCS in MCS + Vehicle rats: ρ value = 0.8143, P = 0.04). (D) Comparison of pre- and post-withdrawal threshold changes in the MCS with the vehicle injection group. Vehicle injection did not affect the MCS effects. (E) Comparison of pre- and post-withdrawal threshold changes in the MCS with the ZIP injection group. ZIP injection abolishes the effects of MCS.
