Figure 1.
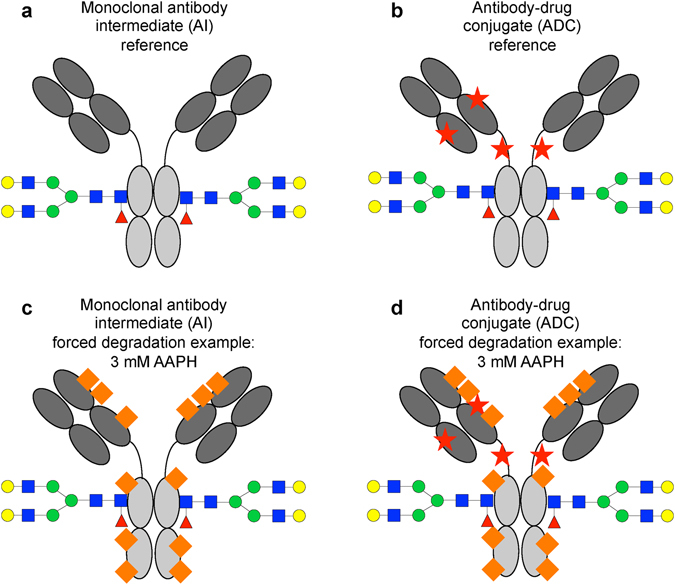
Overall experimental design. (a) Schematic representation of a reference antibody intermediate (AI) sample (gray), and its modifications such as N-linked glycosylation (colors). (b) Schematic representation of a reference antibody drug conjugate (ADC). The ADC is an immunoglobulin G1-kappa monomethylauristatin E (MMAE) conjugate, where one or more of the inter-chain disulfide bridges of the AI were intentionally chemically modified to an average of three to four linker-drug-modified cysteine residues (red stars). The conjugation was not expected to impact post-translational modifications of the AI. More than 34 post-translational modifications were considered herein, and enriched minor variant samples were generated for some modifications. (c) Schematic representation of one of the forced degradation conditions (e.g., 3 mM AAPH) applied to AI. The forced degradation introduces modifications such as oxidation (orange rectangles). (d) Schematic representation of one of the forced degradation conditions (e.g., 3 mM AAPH) applied to ADC. As in AI, forced degradation introduces modifications such as oxidation (orange rectangles). The Fab (dark gray) and Fc (light gray) regions of the molecules are shown for clarity.
