Figure 6.
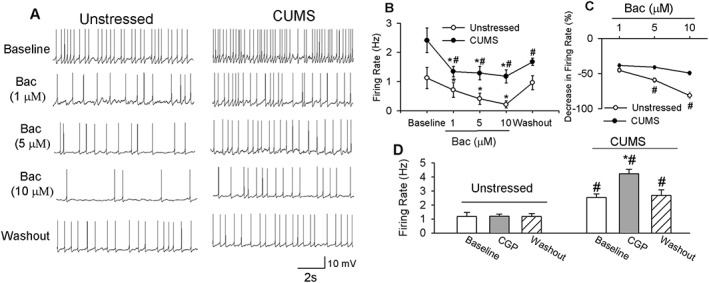
CUMS blunted the inhibitory effect of baclofen (Bac) on PVN‐CRH neurons. Raw traces (A) and summary data (B) show that baclofen dose‐dependently decreased the firing activity of PVN‐CRH neurons. Baclofen induced a smaller inhibition of PVN‐CRH neurons (n = 12 neurons) in seven CUMS rats than in unstressed rats (n = 13 neurons in seven rats). (C) Summary data show the percentage inhibition of firing activity of PVN‐CRH neurons in both CUMS and unstressed rats. (D) Summary data show that CGP55845 (CGP) (2 μM) had no effect on the firing rate of PVN‐CRH neurons (n = 10 neurons) in seven unstressed rats but increased firing activity (n = 12 neurons) in seven CUMS‐treated rats. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, significantly different from control within each group; # P < 0.05, significantly different from unstressed rats.
