Figure 2.
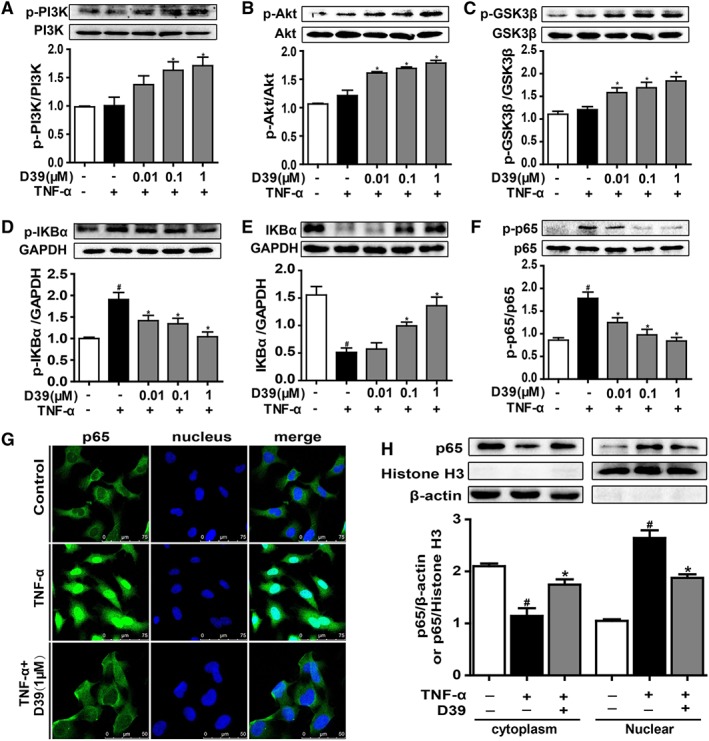
D39 activated the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and inhibited NF‐κB p65 nuclear translocation in endothelial cells. HUVECs and primary HUVECs were treated with TNF‐α (10 ng·mL−1) and D39 (1 μM) for different durations and lysed. (A–C) PI3K, Akt and GSK3β as well as phosphorylated PI3K, Akt and GSK3β were assessed by Western blots. (D–F) IκBα and p65 as well as phosphorylated IκBα and p65 were assessed by Western blots. (G) Immunofluorescence staining of NF‐κB p65 in primary HUVECs after treatment with 1 μM D39 for 1 h followed by 30 min stimulation with TNF‐α (10 ng·mL−1) or vehicle. Scale bar, 50 μm. (H) NF‐κB p65 protein expression in the cytoplasm and nucleus of D39‐treated primary HUVECs. Cells were pretreated with 1 μM D39 for 1 h and stimulated with TNF‐α (10 ng·mL−1) for 30 min. Proteins were extracted from the cytoplasm and nucleus, using β‐actin and histone H3 as the internal standards. Data shown are the means ± SEM (n = 5 in five individual experiments) for the cell line experiments. # P < 0.05, significantly different from the unstimulated group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from the TNF‐α‐stimulated group.
