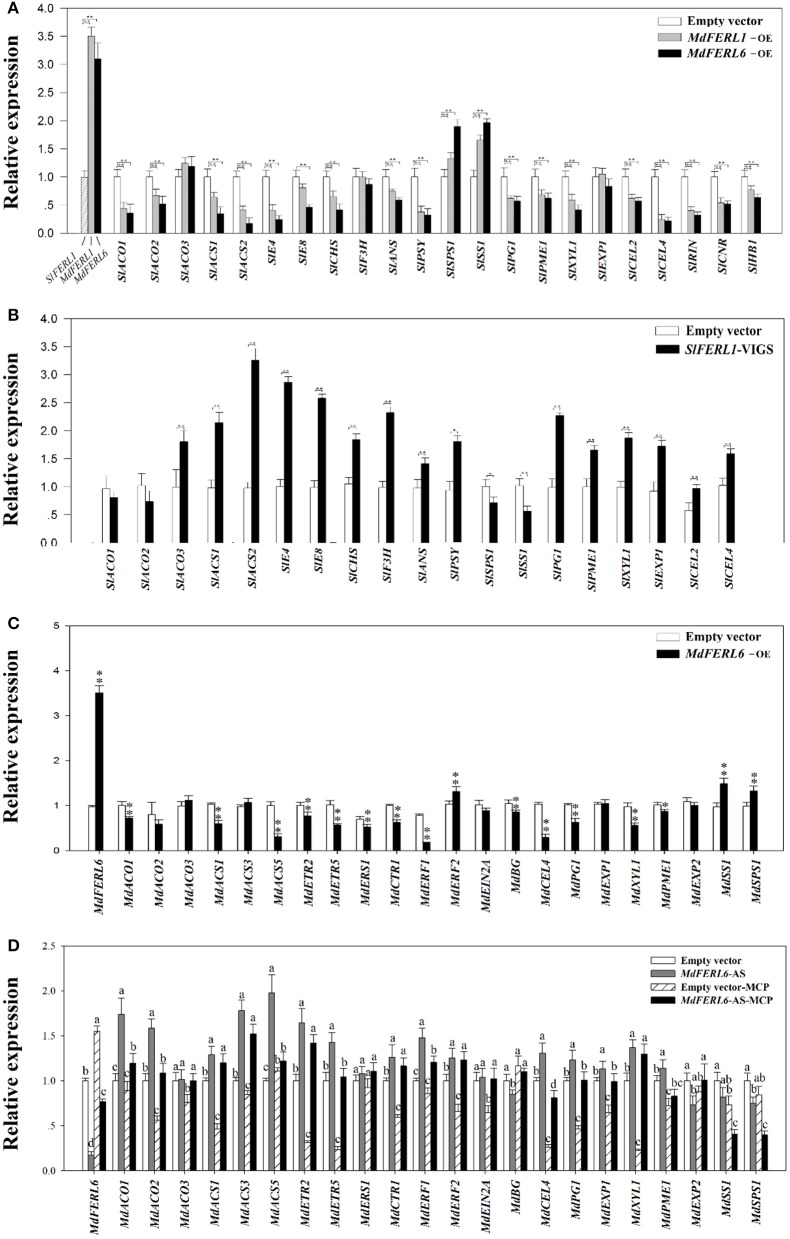
Figure 6.
Effect of MdFERL1, SlFERL1, and MdFERL6 on the expression of ripening-related genes. (A) Effect of MdFERL1 and MdFERL6 on the expression of tomato ripening-related genes. The MdFERL1-OE (overexpression) and MdFERL6-OE constructs were injected into tomato fruits at 18 DPA and gene expression was analyzed 10 days after transfection. Control samples were transfected with the empty vector (pCambia1304). RT-qPCR was conducted using SlACTIN as an internal control. Values are means + SD of three biological replicates. Double asterisks denote a significant difference at **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 using Student's t-test. (B) Effect of SlFERL1-VIGS (virus-induced gene silencing) on the expression of tomato ripening-related genes. The VIGS constructs were injected into fruits at 18 DPA, and gene expression was examined 12 days after transfection, using RT-qPCR. SlACTIN was used as the internal control. Values are means + SD of three biological replicates. Double asterisks denote a significant difference at **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 using Student's t-test. (C) Effect of MdFERL6-OE on the expression of ripening-related genes in apple calli. RT-qPCR was conducted using MdACTIN as an internal control. Values are means + SD of three biological replicates; different lowercase letters represent significant differences based on ANOVA (P < 0.05). (D) Effect of MdFERL6-AS and MdFERL6-AS combined with 1-MCP on the expression of ripening-related genes in apple calli. RT-qPCR was conducted using MdACTIN as an internal control. Values are means + SD of three biological replicates; different lowercase letters represent significant differences based on ANOVA (P < 0.05).